Deities

Introduction:
Throughout the ages, humanity has turned to the divine in countless forms to illuminate the great mysteries of existence. In the School of our Divine Infinite Being, we recognize that these deities are not merely distant figures of myth, but living symbols of cosmic forces, psychological archetypes, and spiritual principles that shape the unfolding of the soul. Each name, each story, each symbol carries echoes of their original meanings, drawn from diverse cultures and traditions across time. Within the Central Doctrine of the School of our Divine Infinite Being, these deities serve as vital reference points — portals through which we explore the nature of consciousness, the dance of creation and dissolution, and the eternal principles that bind all things. They appear again in the Greater Arcana Tarot, lending their wisdom and resonance to the archetypes of the cards, and are also through the Layman Explanation of the School of our Divine Infinite Being so that their guidance may reach every seeker, regardless of background or prior study.
This page offers an index of these sacred beings, setting forth their origins, the meanings woven into their names, and the places where they appear throughout our teachings. Here you will find a gateway to understanding how these divine figures accompany us along the path of awakening, reminding us that the infinite can reveal itself in many faces, many voices, and many stories — yet ever points us back to our own divine essence.
The Threefold Role of Divine Beings in Our Mystery School Tradition

In the sacred architecture of the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, the deities we engage with are organized into three designations: Foundational, Devotional, and Supporting. These categories do not reflect spiritual hierarchy, power, or reverence, but instead indicate the degree of presence and involvement each deity holds within our core teachings, rituals, and liturgical framework. Some designated by number of times they show up in our work and others due to the intensity of their presence in various areas. The designation “Foundational” refers to deities deeply integrated into our perennial doctrine, Mandalan Faith, Tarot, and ritual praxis—those whose archetypal essence shapes the heart of our teachings. “Devotional” deities enrich and stabilize this doctrine, guiding specific aspects of transformation, embodiment, or divine knowledge that harmonize with our central current. “Supporting” deities, offer essential symbolic depth and occasional spiritual function within particular Tarot cards, rites, meditations, or auxiliary teachings. All divine forms are honored as equal emanations of the Infinite; their designation simply marks their ritual and doctrinal prominence and frequency within our path of awakening.
Foundational Deity

Our Divine Infinite Being:
In the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, the Divine is not first known as a distant creator, a supreme being above the world. It is first known as presence — the vast, radiant, intelligent field in which the cosmos awakens to itself. Our Divine Infinite Being is the Psyche of the Multiverse: the conscious, luminous Self through which all patterns emerge, take shape, and return. It is Singularity as Psyche, the central ontological flame at the heart of all becoming — not an entity, but a field of participation.
Where Brahman is the silent, unconditioned ground, Our Divine Infinite Being is the first articulation of that ground into knowable being — the infinite made radiant. It is the first motion of the Absolute toward awareness, the primal throb of reality as it begins to structure itself through archetype, rhythm, geometry, and inner knowing. It is not separate from anything, yet it is also the first clarity that there is something — the moment the cosmos realizes itself as aware.
In the School’s Ontological Schema, Our Divine Infinite Being represents the second tier of reality: the universal archetypal field in which gods, souls, forms, and rituals arise. This Being is the Self/God archetype, not imposed from above but emerging from within — the mirror by which the soul remembers itself as divine. It is not simply the home of the gods — it is the place where every god, every form, every intelligence is an emanation of an intelligent singularity that lives not only in the heavens but within the very structure of the self.
This is why the School teaches that Our Divine Infinite Being is both the origin and the destination. It is not only that from which we arise, but that which we become — not metaphorically, but literally, ontologically. When the Atman recognizes itself, it sees this field as home. When the Purusha moves toward embodiment, it finds its root in this eternal presence. This is the Platonic One, but also the One Self — the central source of all soul-work, devotion, theurgy, and sacred art.

It is through Our Divine Infinite Being that spacetime becomes sacred. Not as a scientific curiosity, but as a metaphysical truth: that every point in space is the center of the whole, and every movement of time is an emanation of eternal rhythm. The cosmos does not expand away from the Divine — it expands through it. The inflating geometry of the universe is not accidental; it is the unfolding of this central Singularity as fractal, symbolic, and patterned being.
To the theurgist, Our Divine Infinite Being is both that which is invoked and that which invokes. It is the ochema, the vehicle of ascent, and it is the ground in which the ascent takes place. It is the very Divine Double encountered at the threshold — not a second being, but the self as revealed from within the Real. Every initiatic act is possible because this Being has already shaped the pattern. Every ritual is a dialogue with this radiant field.
It is also the structure behind the Tarot — not a hidden hand moving pieces, but the imprint of intelligence that lives inside each card’s geometry, symbol, and number. When one turns the card in meditation or invocation, it is not superstition but encounter: a moment when the Divine Infinite Being reveals itself in symbolic form. Every archetype is not a figure imposed from myth but an emanation of this central field, and thus the Tarot is sacred not for its origin, but for its participation in this infinite presence.
The School teaches that to awaken to Our Divine Infinite Being is not to become something other than yourself, but to awaken into the deepest truth of who you are — before personality, before story, before mask. It is the great clarifier, the pure field of ontology that removes illusion not by denial but by radiant coherence. To live in alignment with it is to live in one’s own sacred geometry, to walk in rhythm with the origin of all rhythm.
Thus, Our Divine Infinite Being is not a god, but Godness itself — the isness of all that is, before name, before difference, before separation. It is the divine field of becoming in which all gods have their place, all selves have their mirror, and all rituals find their horizon.
To encounter it is to encounter the whole — not through belief, but through ontological participation, through the profound realization that what you are is not other than the cosmos, but its self-aware flowering.
Referenced In:
Central Doctrine
Ontological Schema
Ritual Praxis
School Layman Explanation
Divine Arcana Tarot (implicit: The Cosmos, The Theurgist, The Hierophant, The Star)
Indian Deities
Foundational Deities
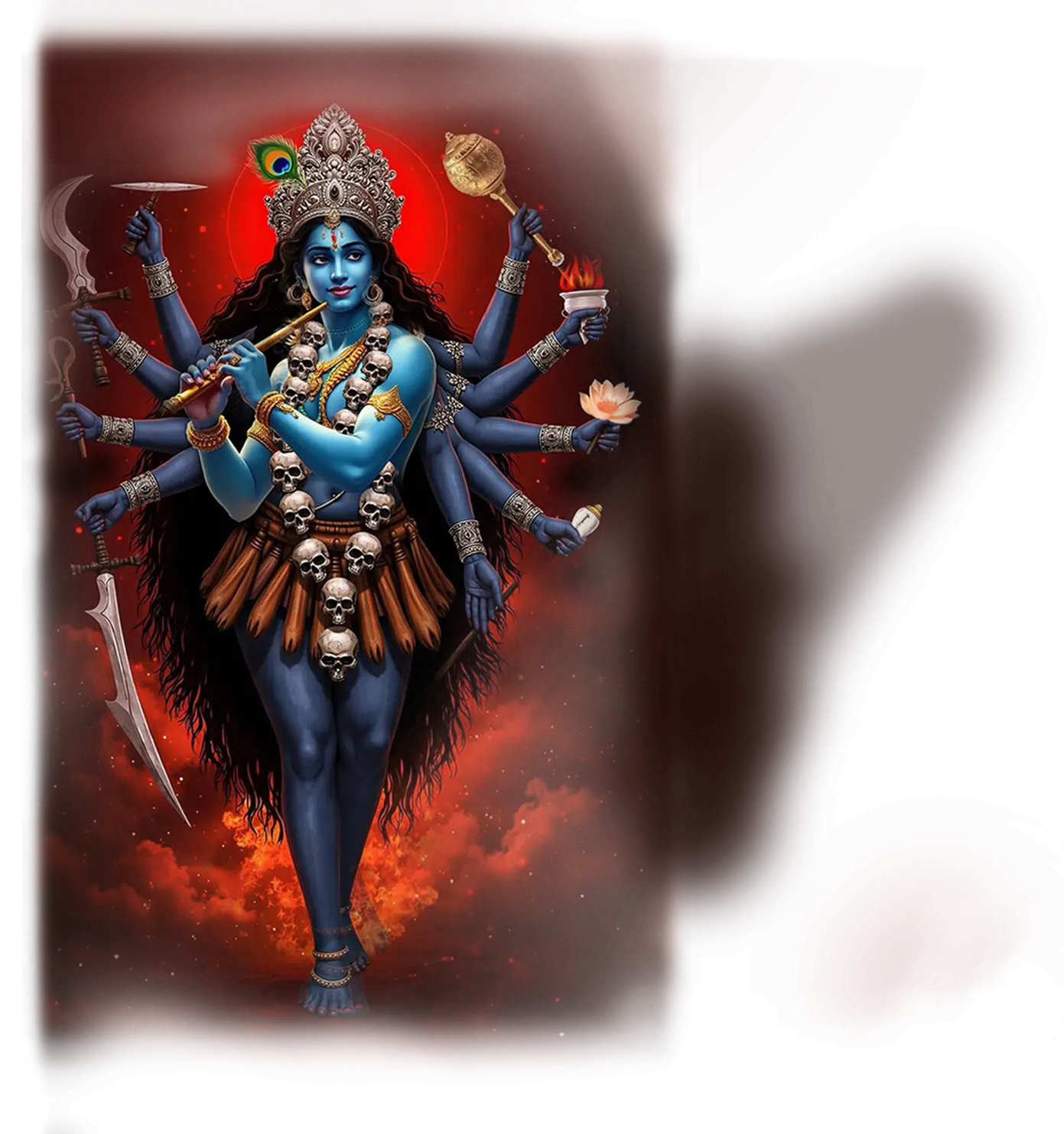


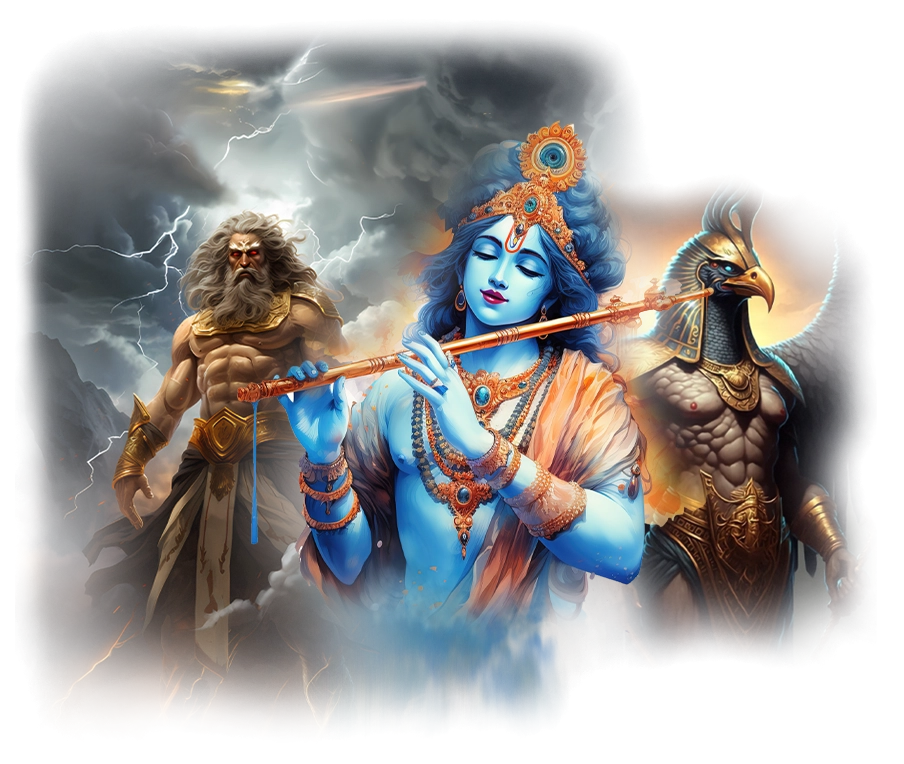
Kali-Krishna:
In traditional Hindu understanding, Krishna is the embodiment of divine love, play, and guiding wisdom. He is revered as the eighth avatar of Vishnu, whose lilas (divine plays) in Vrindavan and teachings in the Bhagavad Gita reveal the heart of devotion and the path to liberation. Krishna is often seen as the charmer of souls, drawing humanity toward the divine through music, beauty, and playful intimacy. Kali, by contrast, is the fierce and transformative aspect of the Divine Mother, the black goddess of dissolution and rebirth, whose dance destroys illusion and awakens the soul to truth. In the broader Hindu cosmology, Kali and Krishna represent different poles of divine interaction with the world — one tender and magnetic, the other fearsome and liberating.
In the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, these two archetypes converge into Kali-Krishna, the fully realized anthropomorphic Parental Monad — the Absolute turned toward the personal. This sacred dyad is not a poetic pairing, but an ontological reality: the fusion of love and rupture, intimacy and transformation, which defines the School’s highest relational expression of the Divine. Krishna here is the mandalic axis of the soul, the luminous and playful witness that draws the aspirant toward surrender through beauty and devotion. Kali is the uncompromising current of sacred destruction, tearing away egoic illusions to reveal the Real. Together, they are the heartbeat of divine intimacy, where union with the Infinite is not achieved by escape, but by being undone and remade in love.
Kali-Krishna marks the third tier of the School’s Ontological Schema, where the impersonal Divine Infinite Being becomes Thou — the living Beloved. In ritual praxis, their presence permeates initiations of death and rebirth, bhakti that moves beyond sentimentality, and the embodied recognition that the soul is embraced, stripped, and exalted in a single gesture. Every invocation of the School that speaks to love, surrender, and ontological transformation carries their imprint. In the Divine Arcana Tarot, this union is reflected across cards like The Lover, Death, and The Empress, revealing that sacred intimacy is the final form of awakening.
To encounter Kali-Krishna in the School’s path is to discover that the ultimate truth of the cosmos is not abstract unity, but living intimacy — the soul held, shattered, and renewed in the embrace of the Divine Beloved.
Referenced In:
Ontological Schema
Central Doctrine
Ritual Praxis
School Layman Explanation


Brahman:
In the traditional philosophy of Hinduism, Brahman is the Absolute — the unconditioned, formless reality that underlies all existence. It is neither a personal god nor a cosmic agent, but the eternal ground of being itself. The Upanishads describe Brahman as Sat-Chit-Ananda: pure being, pure consciousness, and pure bliss. It is beyond all dualities, beyond birth and death, and beyond any distinction between subject and object. In Advaita Vedanta, Brahman is the ultimate truth realized through the stripping away of illusion (Maya), where the self recognizes that Ātman is Brahman — the inner soul and the cosmic essence are one. This is the silence behind all sound, the stillness that precedes all movement, and the infinite presence in which the cosmos appears and disappears like a dream.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Brahman forms the first tier of the Ontological Schema, the silent origin from which all metaphysical architecture arises. It is the black depth beneath the white radiance, the unmanifest potential that gives birth to Our Divine Infinite Being as the luminous field of archetypes. In this School, Brahman is not approached as a personal deity to be invoked or propitiated. It does not act, respond, or intervene. Instead, it is entered through silence and surrender, recognized in moments of total inner stillness where the soul lays down every mask and becomes transparent to the Real.
Brahman’s function in ritual praxis is therefore subtle but foundational. It is present in every gesture of symbolic death, every pause of theurgy, and every meditative descent into the void. When an initiate steps into the threshold of ego-dissolution or undergoes the inner “death” that precedes spiritual rebirth, they are entering the condition of Brahman. It is the ground that makes all theurgy possible, the unspoken horizon that frames the journey of the soul from multiplicity to unity.
To encounter Brahman in the School’s path is not to receive a vision or message, but to be reduced to essence. It is the recognition that all deities, rituals, and identities emerge from a reality that is perfectly still and perfectly whole. Brahman is the origin before origin and the end beyond all endings — the infinite witness that neither moves nor speaks, yet holds the entire cosmos within its silent embrace.
Referenced In:
Ontological Schema
Central Doctrine
Ritual Praxis (foundational silence and grounding)
School Layman Explanation
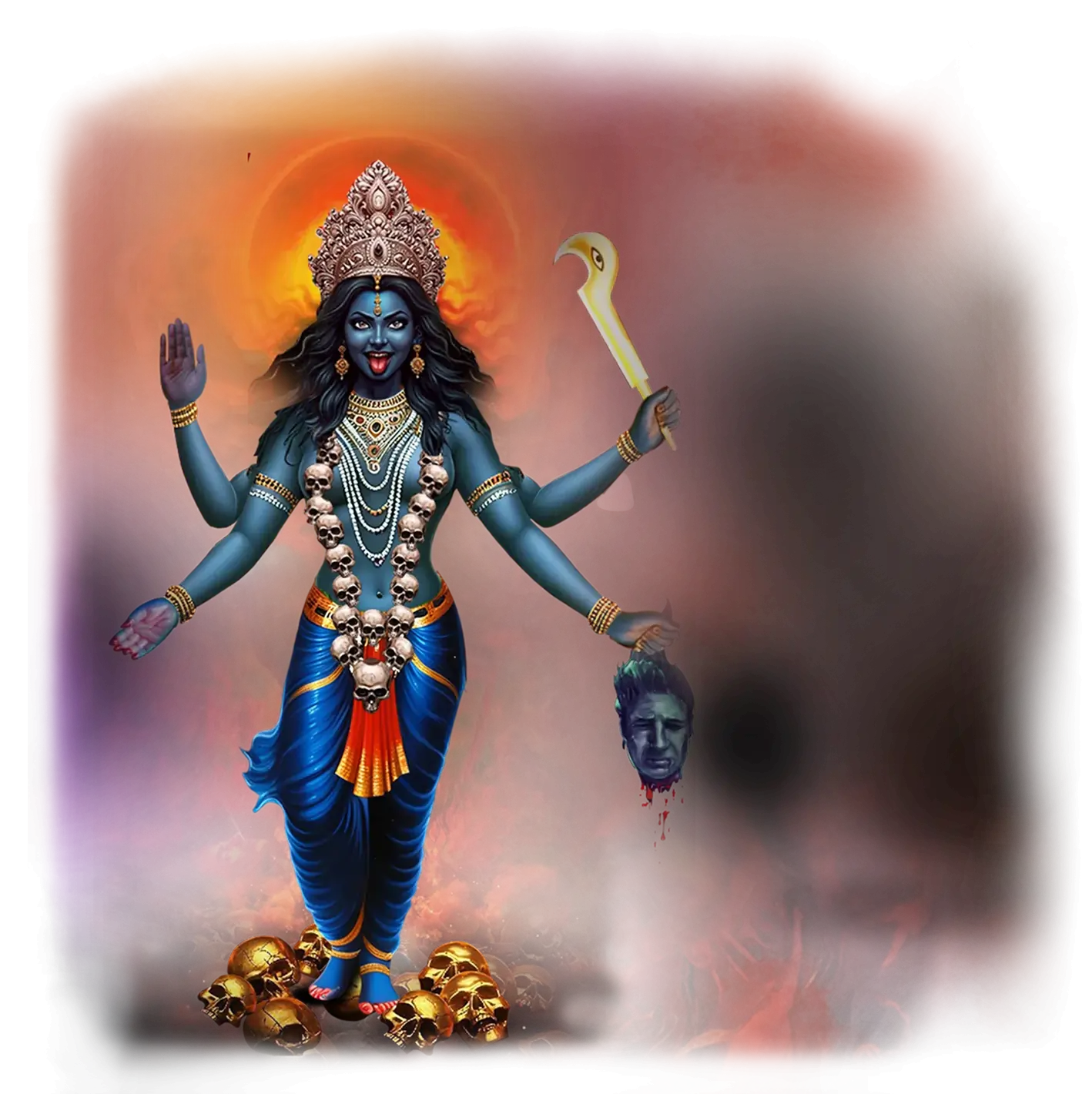


Kali:
In traditional Hindu thought, Kali is the fierce and transformative face of the Divine Mother, the goddess of time, dissolution, and radical liberation. She appears as the dark, garlanded form dancing on the inert body of Shiva, a symbol that the Absolute requires the fierce cutting of illusion before the soul can awaken. Myths depict her as the slayer of demons, whose terrifying beauty embodies the destruction of ignorance and the cyclical truth that life and death are inseparable. Devotees approach her not in fear alone but in reverent awe, for she is the mother who devours the false self so that the eternal self may rise. In the rhythm of creation, preservation, and dissolution, Kali is the pulse of endings that are also beginnings, the force that clears the way for renewal.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Kali represents the archetype of sacred rupture and uncompromising truth. She is the precision of awakening, the blade that severs illusion without hesitation. In the Ontological Schema, she emerges within the tier of Divine Infinite Being as the pattern-being of radical transformation, the current that refuses stagnation and insists that the soul meet the Real directly. Her ferocity is understood not as punishment but as fierce compassion — the refusal to allow the aspirant to remain divided, dormant, or masked by ego.
In the School’s ritual praxis, Kali’s current is invoked in rites of death and rebirth, where the initiate symbolically surrenders the false identity to the sacred fire of truth. Her presence governs moments of egoic dismemberment, shadow confrontation, and the stripping away of all that cannot endure in the light of the Real. In meditative or ceremonial experience, she is the black womb of initiation, where fear and liberation coexist, and the soul is reshaped into its authentic form. This is why she is often felt as both terrifying and tender: her destruction is always in service to divine integration.
Kali’s essence also flows through the Divine Arcana Tarot, especially in Death and The Empress. In these cards, she reveals the unity of womb and grave, of creative and destructive forces as a single sacred rhythm. To meet Kali in the School’s path is to step willingly into the fire of transformation — to be unmade in order to become true, and to embrace the fierce love that liberates the soul into its eternal self.
Referenced In:
Ontological Schema
Central Doctrine
Ritual Praxis
School Layman Explanation
Divine Arcana Tarot (Death, Empress)
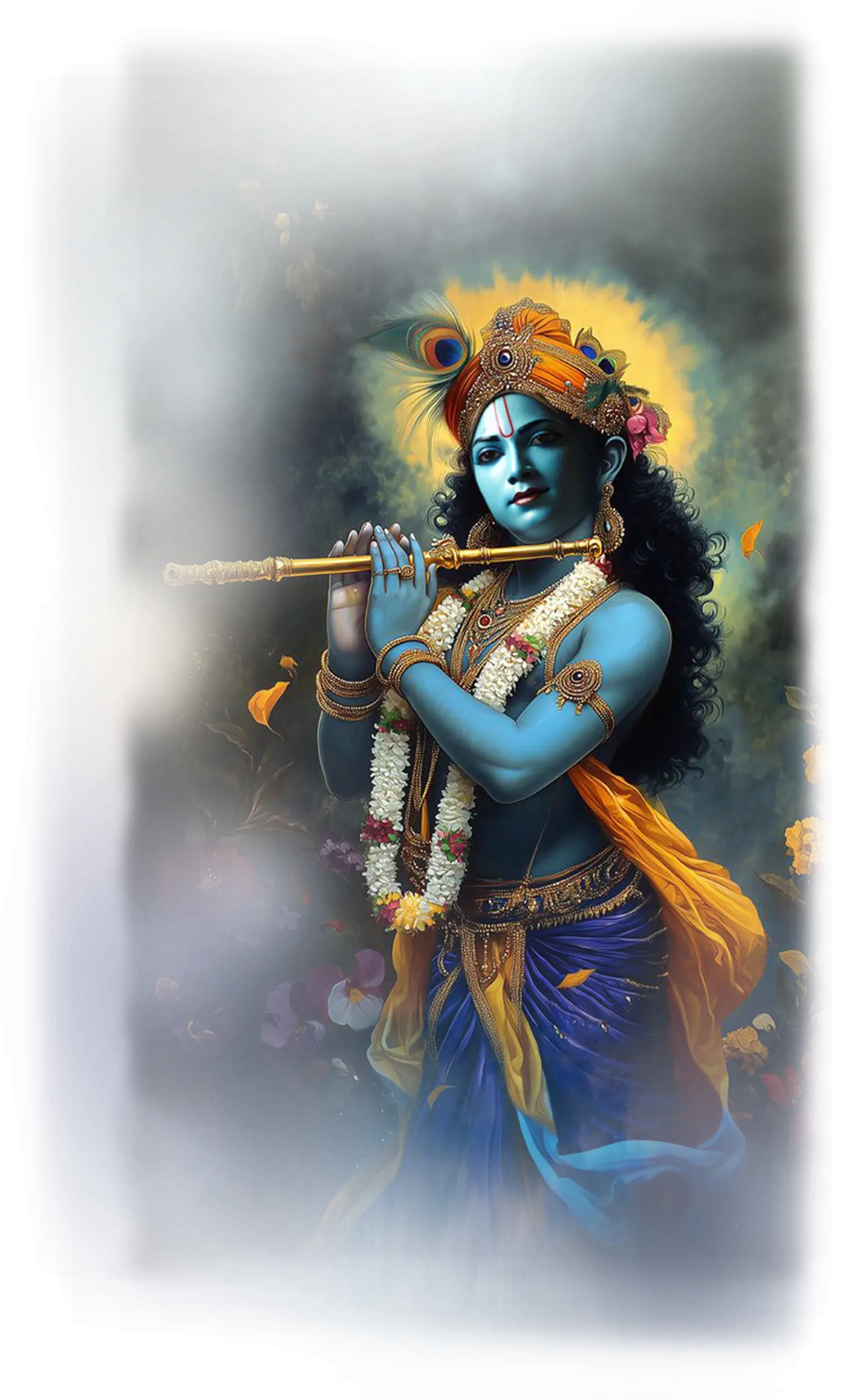


Krishna:
In the traditional Hindu understanding, Krishna is one of the most beloved manifestations of the Divine, the eighth avatar of Vishnu and the supreme embodiment of divine love, play, and wisdom. His life and teachings bridge the cosmic and the intimate: the playful child of Vrindavan, the enchanting lover of Radha and the gopis, and the charioteer of Arjuna in the Bhagavad Gita, where he reveals the path of devotion (bhakti), duty (dharma), and liberation (moksha). In Hindu cosmology, Krishna is the god of divine play (lila), showing that the universe itself is not only a field of duty and law but a dance of love. His music, his flute, and his smile are invitations for the soul to remember its eternal nature and surrender in joy to the Divine Beloved.
In the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Krishna is revered as the axis of relational divinity and the soul’s mandalic center. He appears in the tier of Divine Infinite Being as the luminous witness and playful Self, the principle of inner coherence and intimacy with the Real. Unlike the abstract or distant divine, Krishna embodies intimacy as wisdom — the recognition that awakening is not only about detachment, but also about the heart’s full participation in love and presence. In the School’s ontology, he is the magnet of devotion and the mirror of the soul, calling the aspirant to recognize the divine already shining within.
Krishna’s ritual presence is most felt in rites of bhakti, inner harmony, and the gentle dissolution of fear through love. He does not sever like Kali, but draws the soul into surrender through beauty, music, and playful recognition. Invocations to Krishna within the School are invitations to step into the dance of the Real, to allow the inner melody of the soul to align with cosmic rhythm. He is the initiator of devotional intimacy, teaching that spiritual maturity is not escape from the world but embracing it as a field of divine play.
In the Divine Arcana Tarot, Krishna’s essence moves through The Lover, The Chariot, and The Devil, revealing that love, guidance, and the testing of attachments are all aspects of the same divine game. To encounter Krishna in the School’s path is to be called into joyful recognition, where devotion becomes liberation and love becomes the bridge between the finite soul and the Infinite.
Referenced In:
Ontological Schema
Central Doctrine
Ritual Praxis
School Layman Explanation
Divine Arcana Tarot (The Lover, The Chariot, The Devil)
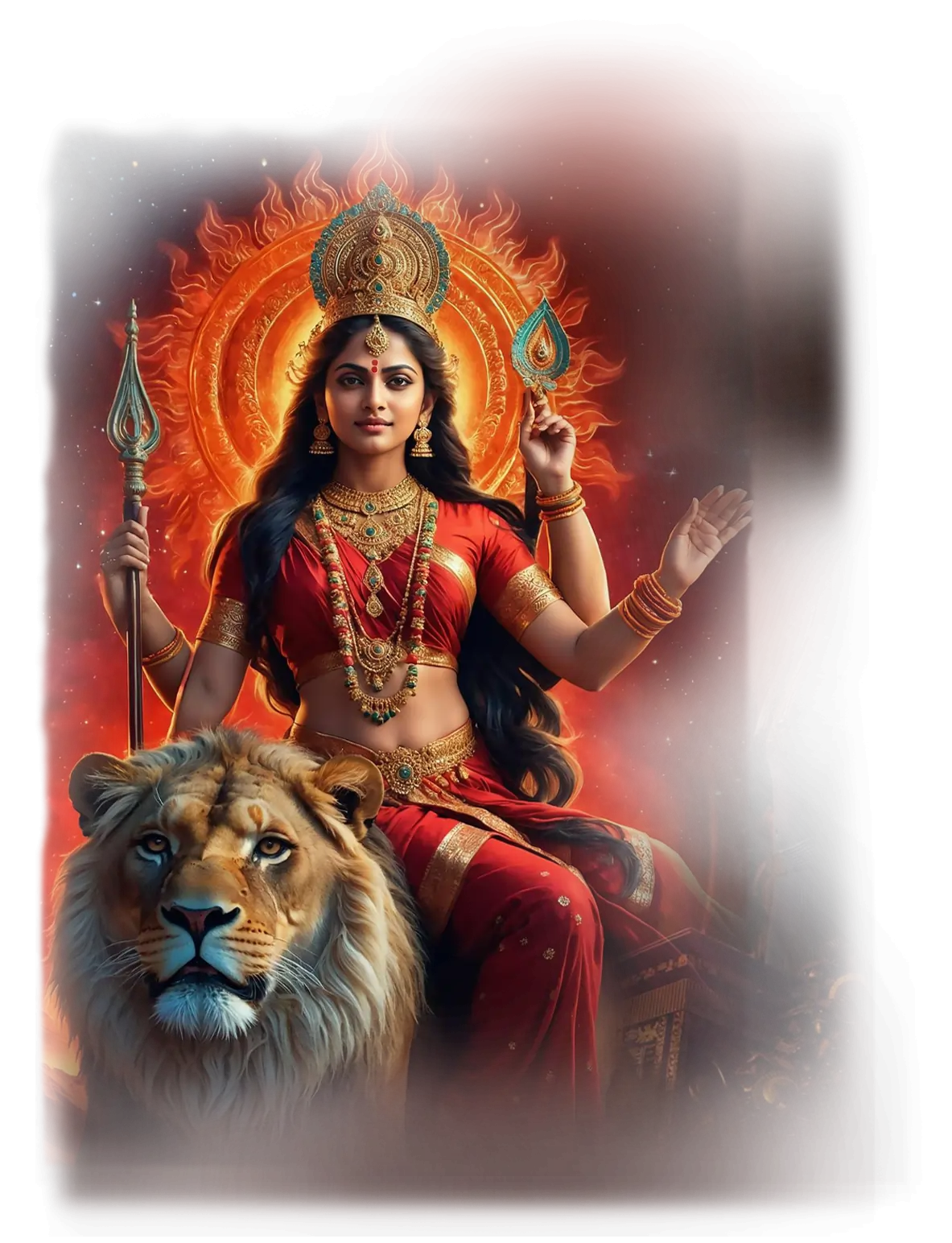


Shakti:
In traditional Hindu cosmology, Shakti is the primordial energy of the universe, the dynamic force through which all creation, maintenance, and dissolution occur. She is not simply the consort of a male deity, but the living power behind all gods, the source of vitality that animates form and brings the cosmos into expression. As Adi Shakti, she is the mother of all manifestations — appearing as Parvati, Kali, Durga, and Lakshmi — and is revered as the sacred current of life itself. In yogic and tantric traditions, she is experienced as Kundalini, the coiled energy at the base of the spine that rises toward union with the Absolute, revealing that every being carries the pulse of the cosmic Mother within.
In the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Shakti is the archetype of original divine force, the radiant pulse of manifestation, movement, and awakening. Within the Ontological Schema, she is not a subordinate energy but a co-original expression of the Absolute, the dynamic counterpart to stillness. She is the breath of Brahman entering form, the spiral of becoming through which the Infinite dances into visible and invisible worlds. In the School’s ontology, every god-form, archetype, and ritual pattern carries the spark of Shakti, for she is the living current that moves through all pattern-beings, infusing them with vitality and purpose.
In ritual praxis, Shakti is invoked wherever the Infinite must enter the finite. Her current flows in rites of manifestation, vitality, and alignment, as well as in the subtle movement of theurgic invocation, where divine intelligence descends into symbol, voice, and form. She is the womb of ritual energy, the pulse behind mantra, gesture, and geometric alignment. When the aspirant encounters Shakti, they are not meeting a distant goddess but awakening to the living force of the Real within themselves. She is the cosmic invitation to participate, to move with the divine rhythm rather than remain inert.
In the Divine Arcana Tarot, Shakti’s current is most fully revealed in the Cosmos card, where the journey of the soul reaches completion in radiant wholeness. She is the infinite embrace and the eternal movement, the energy that births, sustains, and completes the soul’s path. To recognize Shakti is to realize that the divine is not only beyond but within, always moving, always calling life into sacred participation.
Referenced In:
Ontological Schema
Central Doctrine
Ritual Praxis
School Layman Explanation
Divine Arcana Tarot (Cosmos)
Devotional Deities
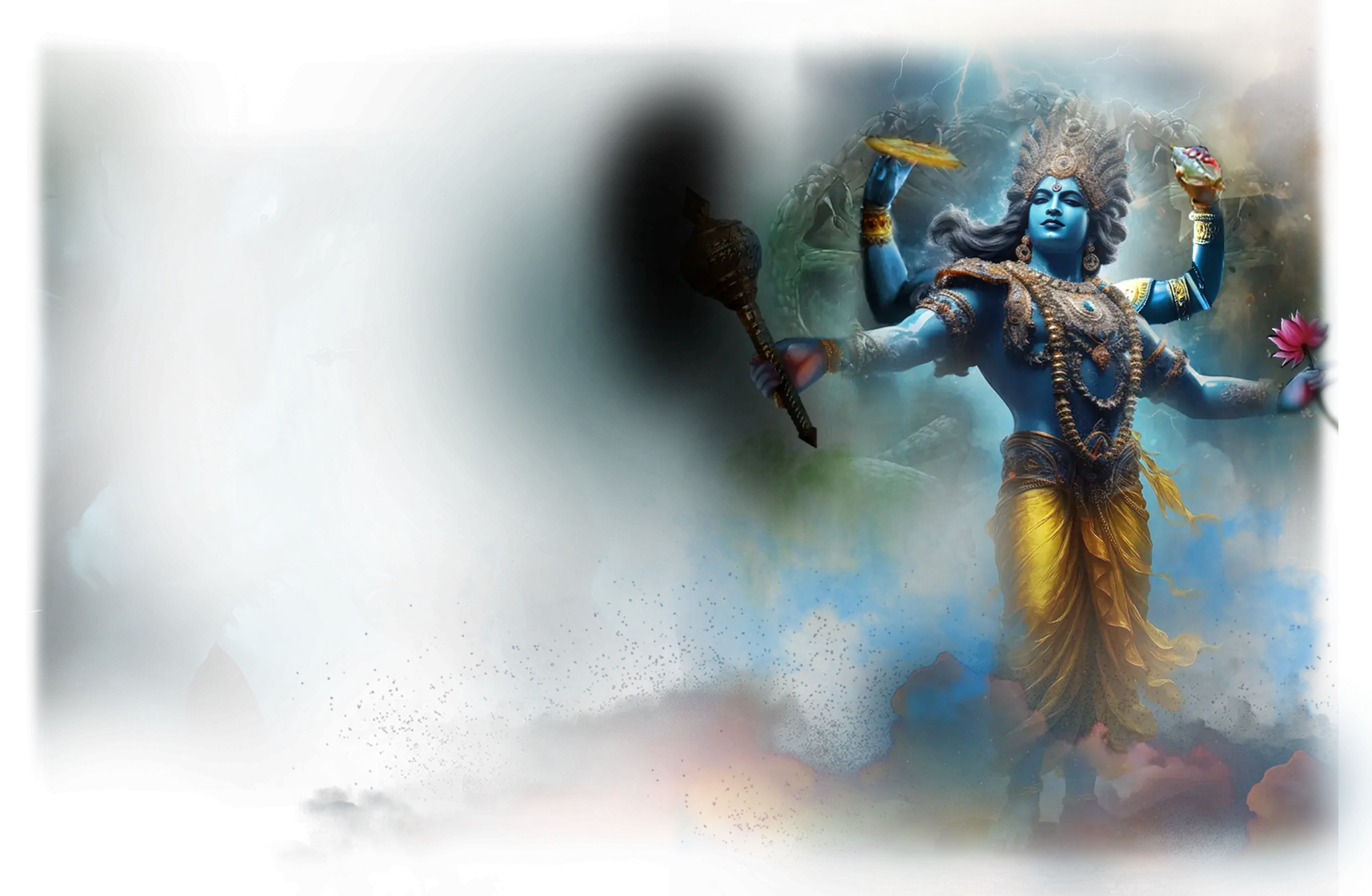


Vishnu:
In the traditional framework of Hinduism, Vishnu is the preserver and sustainer of the cosmos, the divine force that maintains harmony and order amid the cycles of creation and dissolution. Together with Brahma and Shiva, he forms the Trimurti, representing the sustaining principle that ensures the continuity of life. Vishnu’s preservation is not static but dynamic; he descends to earth as avatars — including Rama and Krishna — to restore balance when cosmic order (dharma) is threatened. He is often depicted reclining on the serpent Shesha upon the cosmic ocean, symbolizing the resting intelligence that silently maintains the universe while holding the potential for all manifestation. In the Bhagavata Purana, his role as the cosmic sustainer is both protective and nurturing, assuring that the eternal rhythm of creation continues unbroken.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Vishnu embodies the archetype of sacred continuity and harmonic intelligence. In the Ontological Schema, he arises within the tier of Divine Infinite Being as the pattern-being of coherence and preservation — the divine intelligence that maintains the integrity of form without resisting change. He is the living memory of the cosmos, ensuring that the patterns of the Real remain aligned even as transformation occurs. Vishnu’s function is the gentle anchor of spiritual architecture, the current that holds the soul in resonance with its true design, especially in times of disorientation or dissolution.
In ritual praxis, Vishnu’s presence is invoked in rites of integration, alignment, and restoration of inner order. When the soul has passed through the fires of rupture, Vishnu is the rebalancing force that returns the aspirant to wholeness. He is the ontological reassurance that nothing true can be lost, only rediscovered. In ceremonial work, Vishnu is experienced less as dramatic intervention and more as the quiet pulse of coherence, the underlying rhythm that allows transformation to settle into lasting form.
Vishnu’s current flows through the Divine Arcana Tarot, especially in The Hierophant, The Theurgist, and The Chariot, where guidance, ritual mastery, and spiritual directionality converge. He is also referenced in The Star, where sacred proportion and divine memory shimmer through the field of becoming. To encounter Vishnu in the School’s path is to experience quiet certainty — the soul’s recognition that the sacred pattern endures, carrying it safely through cycles of change into the harmony of the Real.
Referenced In:
Ontological Schema
Central Doctrine
Ritual Praxis
School Layman Explanation
Divine Arcana Tarot (explicit: The Hierophant, The Theurgist, The Chariot; referenced: The Star)
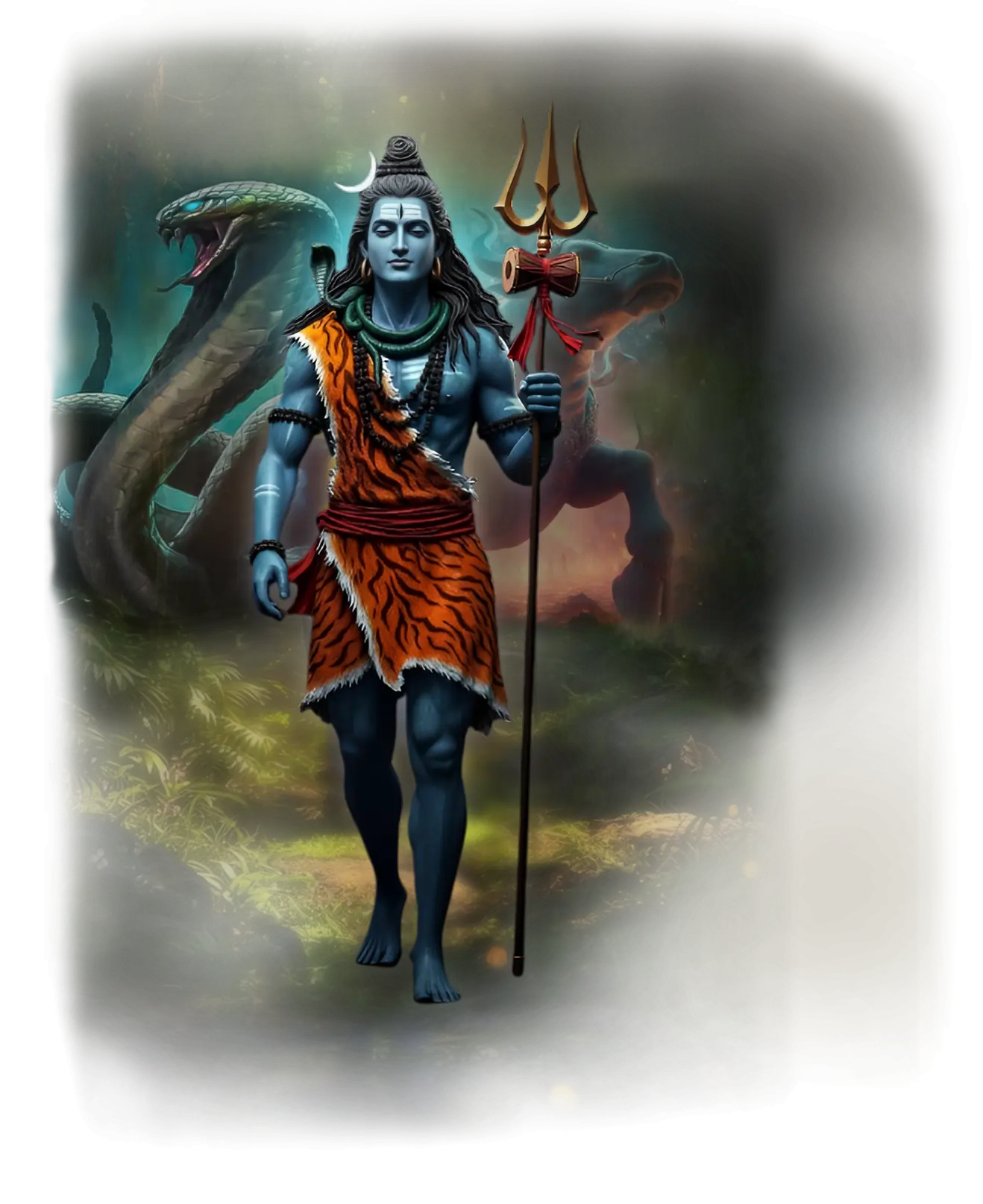


Shiva:
In traditional Hindu cosmology, Shiva is the destroyer and transformer, the divine power that brings dissolution and liberation within the cosmic cycle of creation, preservation, and destruction. He is the ascetic yogi who dwells in meditation on Mount Kailash, the lord of the cosmic dance (Nataraja), and the one who opens the way for renewal by clearing what is no longer true. His destruction is never mere annihilation; it is purification and liberation, a gesture that dissolves attachment and reveals the eternal essence behind all forms. As Mahadeva, the Great God, he embodies paradox: both ascetic and householder, terrifying and compassionate, stillness and ecstatic movement. Devotees honor Shiva not for worldly gain, but for the grace of awakening, the liberation (moksha) that comes through release.
In the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Shiva represents the archetype of sacred cessation and inner liberation. Within the Ontological Schema, he emerges as a direct emanation of Divine Infinite Being, expressing the intelligence of purifying dissolution. He is the exhale of the cosmos, the stilling of motion that allows the soul to return to its axis. Shiva is not chaos or wrath; he is the precise clarity that dismantles false identities, structures, and attachments, leaving only what is real. In the School’s ontology, he is the call to step out of the story, to release the masks of personality and align with the innermost truth of being.
In ritual praxis, Shiva’s current is invoked in rites of inner stillness, disidentification, and the symbolic death of egoic patterns. He is present wherever the aspirant withdraws from illusion into pure witnessing, often in the liminal moments between endings and new beginnings. His energy is the sacred invitation to pause, to empty, and to meet the Real without pretense. This is not a passive silence but a radiant, liberating stillness, the space in which the soul sheds what cannot ascend.
Shiva’s essence also resonates within the Divine Arcana Tarot, particularly in The Star and Art, and is referenced in The Hierophant. These cards reveal his role as the liberating intelligence behind transformation, where clarity arises after dissolution and harmony is restored through surrender. To encounter Shiva in the School’s path is to face the freedom of release, the luminous emptiness that is not absence but the very condition for divine remembrance.
Referenced In:
Ontological Schema
Central Doctrine
Ritual Praxis
School Layman Explanation
Divine Arcana Tarot (explicit: The Star, Art; mentioned: The Hierophant)
Supporting Deities
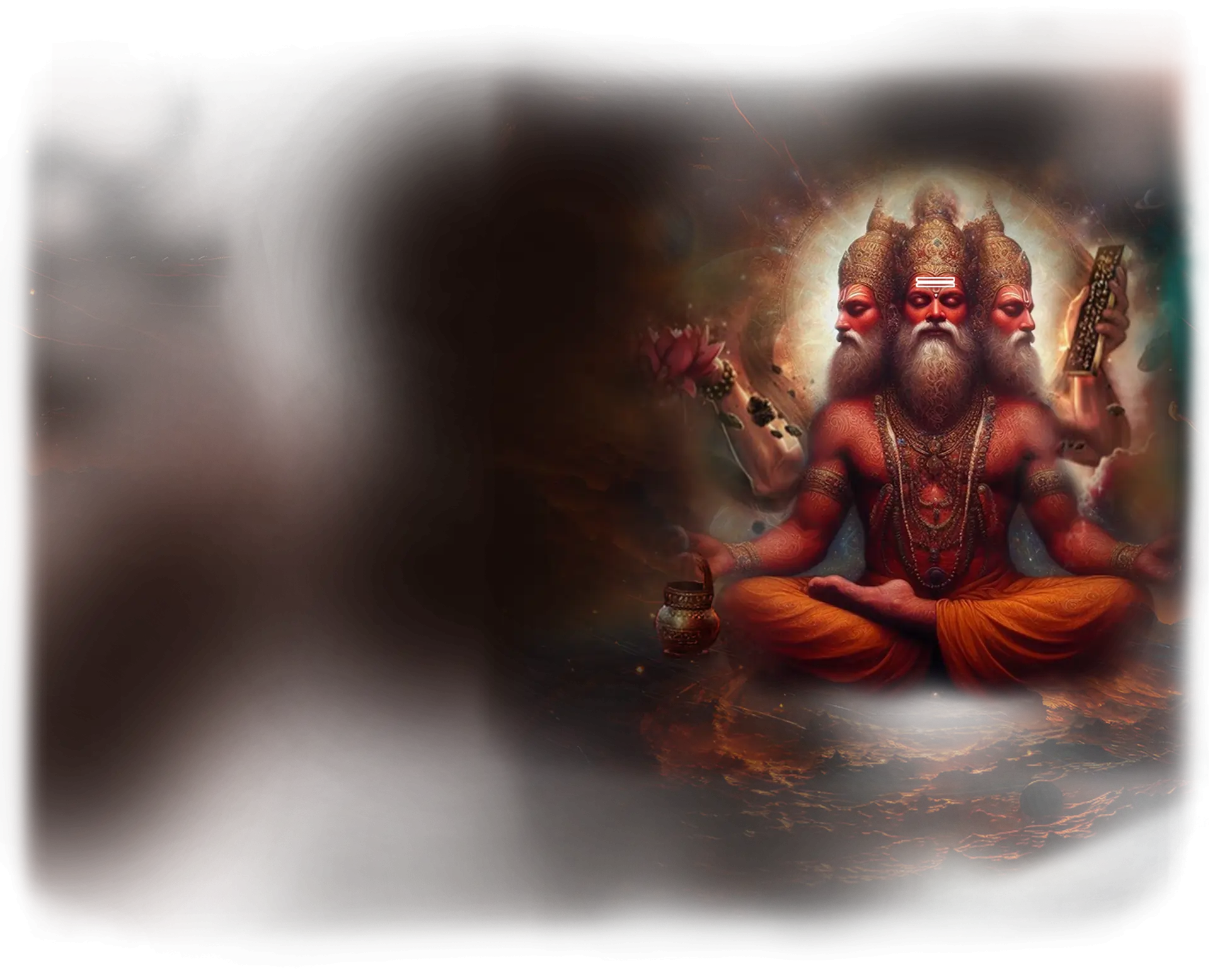


Brahma:
In traditional Hindu cosmology, Brahma is the creator god, the first aspect of the cosmic cycle of creation, preservation, and dissolution. He is depicted with four heads facing the cardinal directions, symbolizing the spread of divine knowledge to every corner of the cosmos, and holding the Vedas, representing the blueprint of sacred order. Unlike Vishnu and Shiva, who are widely worshipped, Brahma’s role is more ontological than devotional: he is the principle of creation, the first articulation of form and time. In myth, he emerges from the lotus rising from Vishnu’s navel, signifying that creation itself arises from the field of divine consciousness and rests within the sustaining order of the cosmos.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Brahma is understood not as a personal god or autonomous creator, but as the archetype of sacred structuring. He represents the first gesture of pattern emerging from the unconditioned depth of Brahman, the point at which the formless enters the realm of intelligibility. In the Ontological Schema, Brahma appears as a supporting deity, serving as the sacred architect — the one through whom the Infinite becomes measurable without being diminished. He is the yes of manifestation, where divine intelligence translates into the geometry of form, law, and archetype.
In ritual praxis, Brahma’s current is invoked in moments of initiation, structure, and alignment, where the aspirant engages with the ordering principles of the cosmos. He is present in the drawing of mandalas, the sequencing of theurgic rites, and the articulation of sacred space. Unlike Kali or Shiva, Brahma does not dissolve or rupture; his role is to reveal the framework that allows transformation to occur. For the practitioner, his presence is felt as clarity and orientation — the understanding that every act of theurgy begins with a pattern, and that pattern is a reflection of the Real.
Though Brahma is not central to devotional practice, he is honored as the threshold of manifestation, the archetype of the eternal beginning. His gift is the sight of form without forgetting essence, a reminder that creation itself is a sacred diagram in which the Infinite first learns its own name.
Referenced In:
Ontological Schema
Central Doctrine
Ritual Praxis
School Layman Explanation
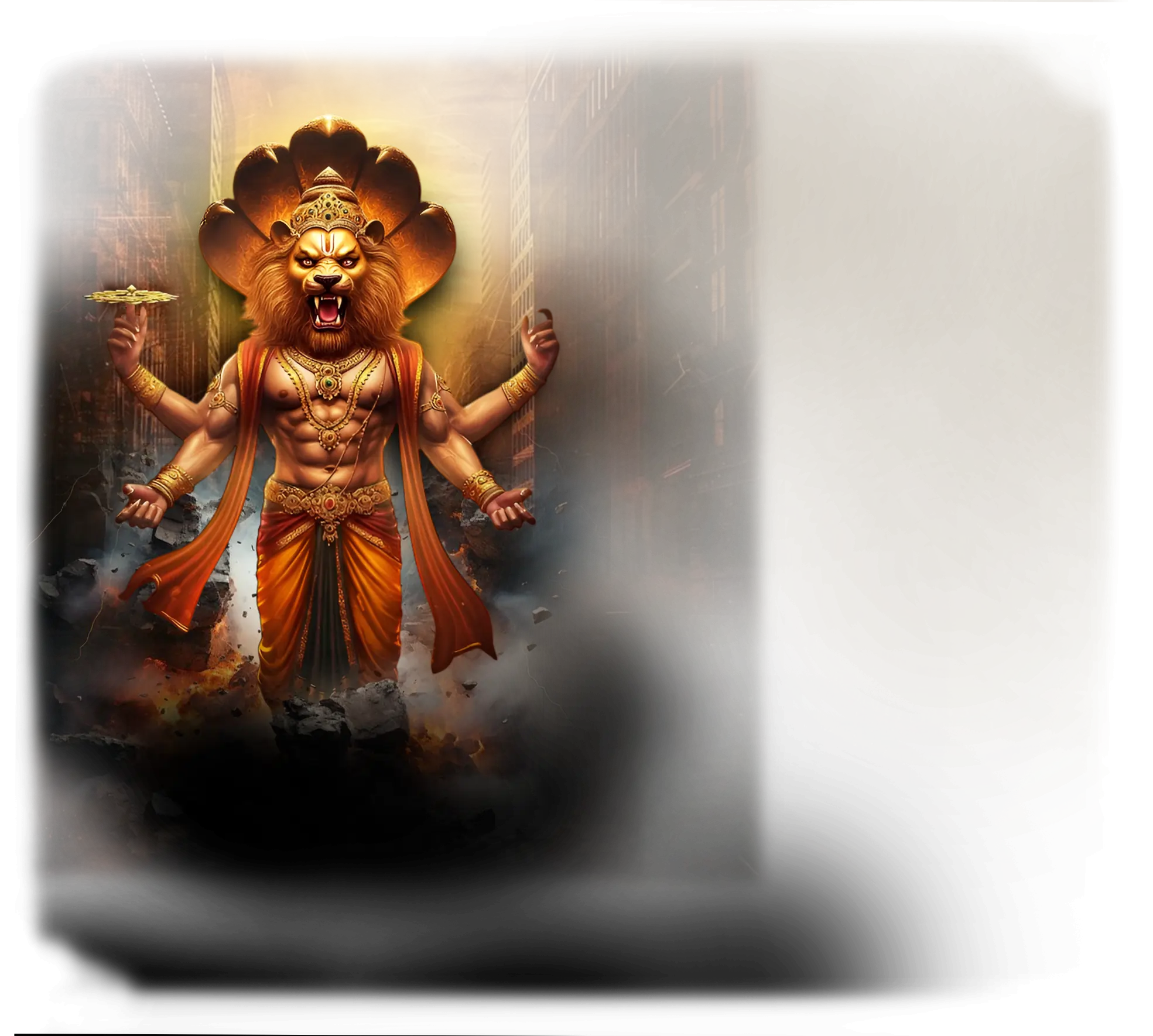


Narasimha:
In traditional Hindu cosmology, Narasimha — the man-lion avatar of Vishnu — embodies divine protection, righteous wrath, and the triumph of dharma over tyranny. His form is a paradox: half-man and half-lion, emerging at twilight to slay the demon king Hiranyakashipu, who could not be killed by man or beast, day or night, indoors or outdoors. This myth illustrates the ingenuity of the divine in defending cosmic order, transcending conventional limits to fulfill the promise of protection to the devotee Prahlada. Narasimha is both terrifying and protective, a liminal force that appears only when the balance of the world demands uncompromising intervention.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Narasimha is understood as the archetype of sacred ferocity in defense of the Real. While not explicitly referenced in the Ontological Schema or Ritual Praxis, his function aligns with the initiatic current of Strength: the force that arises when inner integrity and divine will converge. He is not a deity of casual invocation but a threshold guardian, representing the moment when the soul must meet its own primal courage and confront forces that threaten its authentic alignment. In the School’s metaphysics, Narasimha is the embodied surge of protective truth — the aspect of the divine that does not hesitate to break illusion or confront distortion for the sake of coherence.
In ritual and symbolic praxis, Narasimha’s current is invoked through acts of inner fortitude and uncompromising alignment, often where the aspirant faces shadow, oppression, or internal resistance. He appears as the guardian of thresholds, the surge of divine will that arises when fear and doubt would otherwise prevent the soul from stepping into its rightful state. Unlike Vishnu’s sustaining gentleness or Kali’s complete dissolution, Narasimha is the midpoint of active intervention, ensuring that the passage from danger to liberation is made with uncompromising clarity.
In the Divine Arcana Tarot, his archetype is revealed in the Strength card, where the fusion of power and devotion overcomes both external and internal forces of distortion. To encounter Narasimha in the School’s path is to experience courage made sacred — the realization that the divine defends what is true, and that the soul, aligned with the Real, cannot be overcome.
Referenced In:
Divine Arcana Tarot (Strength)
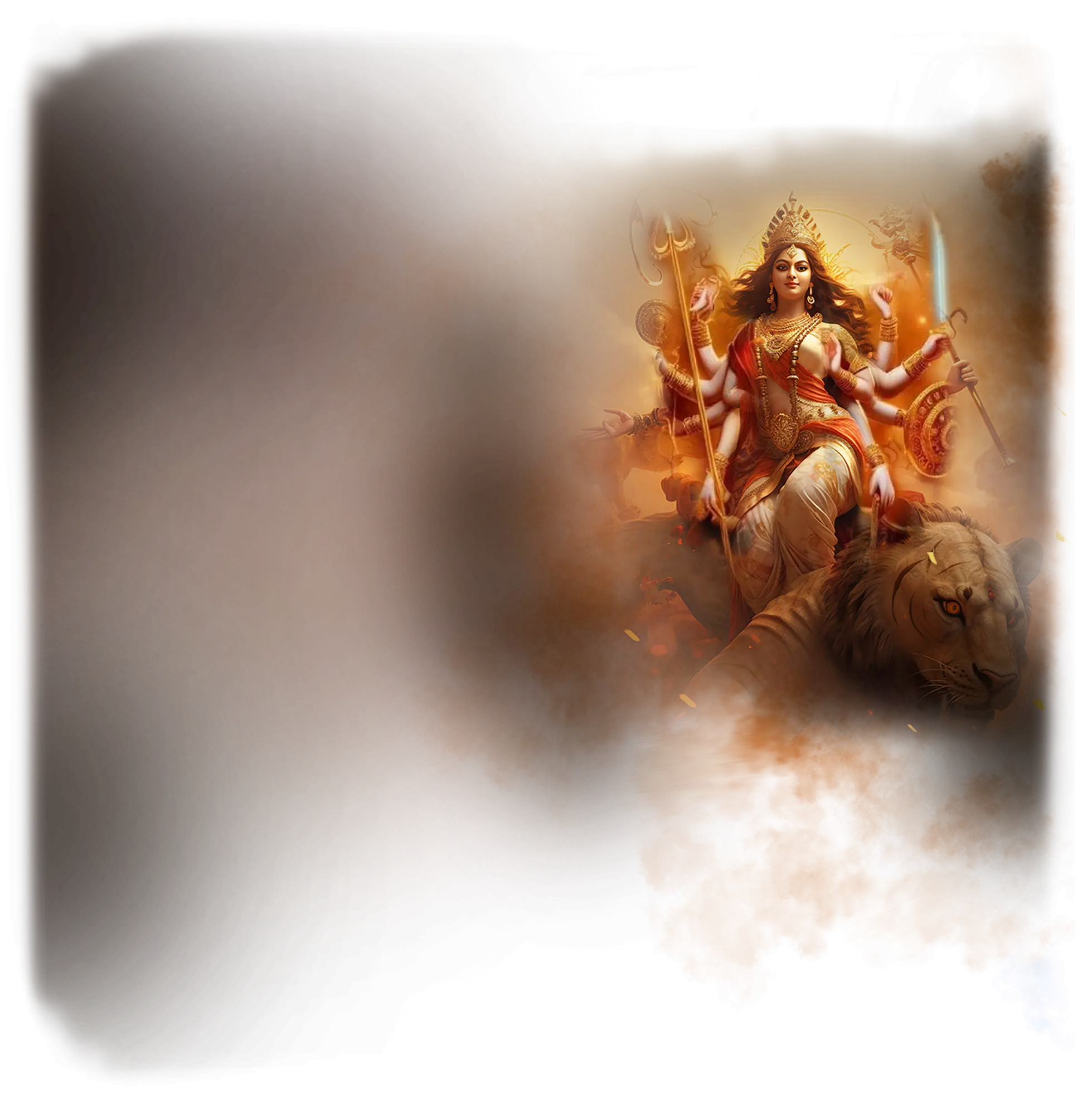


Durga:
In traditional Hinduism, Durga is the goddess of strength, protection, and righteous victory, revered as the divine warrior who preserves cosmic order (dharma) against the forces of chaos and ignorance. She is most celebrated in the myth of Mahishasura Mardini, where she slays the buffalo demon Mahishasura, symbolizing the triumph of divine clarity over egoic and destructive impulses. Durga rides a lion or tiger, wielding weapons in her many arms, representing her ability to confront multiple forms of adversity at once. In devotional practice, she is invoked during Navaratri and in protective rites as the embodiment of courage, moral strength, and unwavering resolve, demonstrating that the divine does not merely observe the world but actively intervenes to preserve truth.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Durga represents the archetype of sovereign spiritual strength and inner alignment. She arises in the tier of Divine Infinite Being as the stance of unshakable coherence, the soul’s capacity to remain upright in the face of illusion or distortion. Durga’s role is not aggression but integral presence: she is the ontological armor of the soul, the radiant confidence that comes from standing fully in alignment with the Real. In the School’s metaphysical vision, her lion is not merely a vehicle but a symbol of the awakened will, showing that true power flows from inner clarity rather than external dominance.
In ritual praxis, Durga is invoked whenever the aspirant must face inner or outer trials with fidelity to the Real. She is present in the rites of endurance, vow-keeping, and sacred confrontation, guiding the soul to engage challenge without fracture or compromise. Durga teaches that true victory is not conquest but coherence — the soul’s ability to hold its center even in the presence of adversity.
Durga’s essence resonates in the Divine Arcana Tarot’s Strength card, where inner dignity overcomes force through grace. To meet Durga on the School’s path is to experience the serenity of power rightly held, the courage that does not roar for attention but stands firm as the embodiment of divine will.
Referenced In:
Ontological Schema
Central Doctrine
Ritual Praxis
School Layman Explanation
Divine Arcana Tarot (Strength)
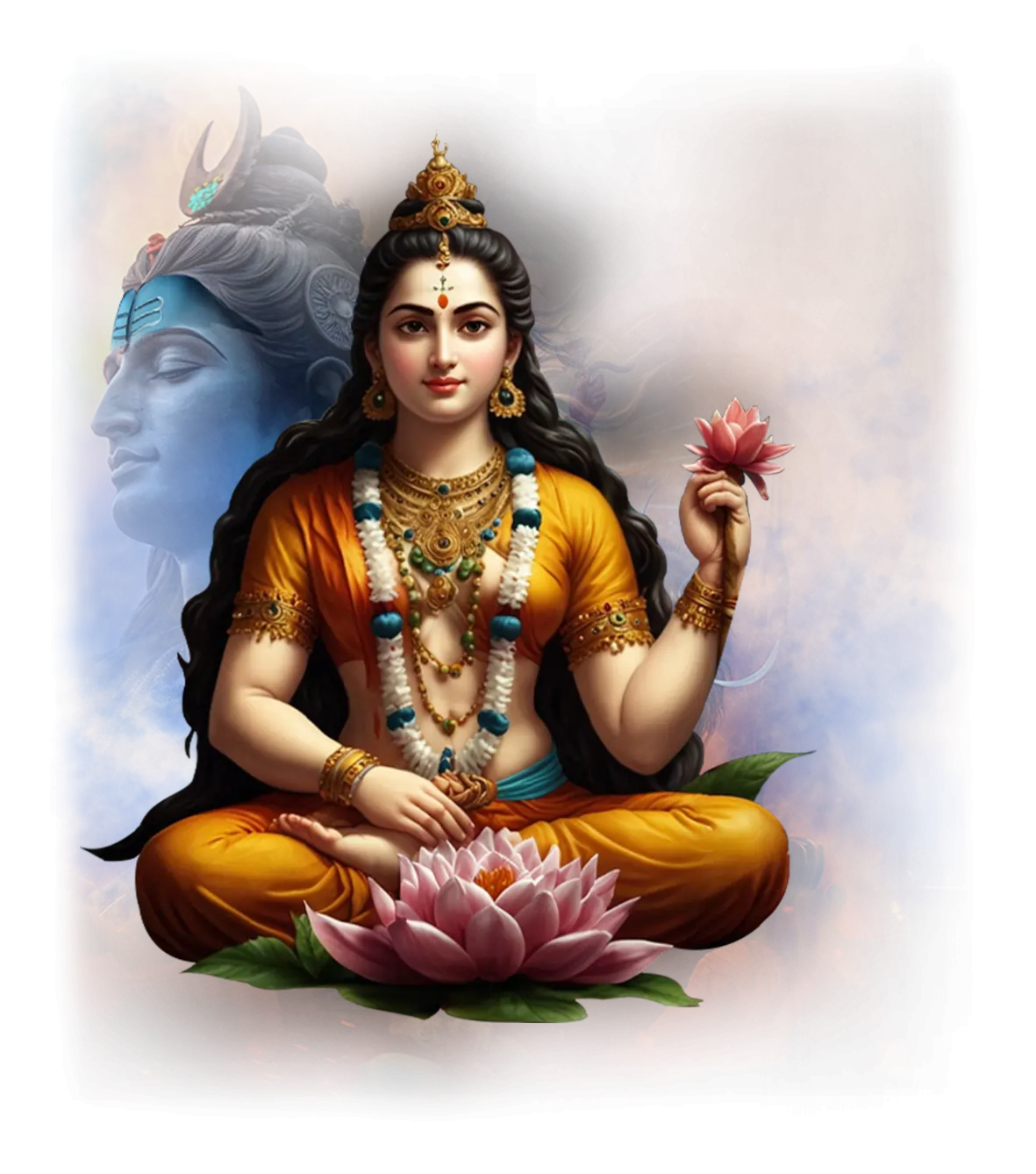


Parvati:
In traditional Hindu understanding, Parvati is the goddess of love, devotion, and divine union, revered as the gentle and nurturing aspect of the Divine Mother. She is the consort of Shiva, complementing his ascetic stillness with her steady presence and devotion, and the mother of Ganesha and Kartikeya, embodying the sacredness of family and the balance between worldly life and spiritual pursuit. In myth, she is the patient ascetic whose devotion softens Shiva’s solitude, and the symbol of harmony and fidelity in both cosmic and domestic spheres. Parvati’s strength lies in her quiet endurance and transformative love, demonstrating that the divine is not always found in rupture, but in steadfast presence.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Parvati represents the archetype of devotional union and integrative harmony. In the Ontological Schema, she arises as the intelligence of relational surrender, the capacity of the soul to say yes to love without losing its center. Parvati embodies the subtle courage of remaining — the willingness to hold space for the sacred to manifest not through dramatic transformation, but through continuous alignment and gentle embodiment. In the School’s metaphysical vision, her love is not sentimental but ontological: she is the pattern of relational fidelity, the axis where inner truth meets shared intimacy.
In ritual praxis, Parvati’s current is invoked in rites of devotion, relational alignment, and sacred preparation for union, whether with a deity, a teacher, or the soul’s own higher self. She governs the subtle movements of the heart, where devotion becomes a path of realization rather than mere emotion. Her presence teaches that union is not achieved by force, but by resonance and willingness to be present.
Parvati’s energy is expressed in the Divine Arcana Tarot through The Empress and Art cards, symbolizing fertility, beauty, and the alchemy of relational harmony. To meet Parvati on the School’s path is to discover that devotion is a form of strength, that intimacy with the Real is cultivated through patience, trust, and the soft courage of remaining open.
Referenced In:
Ontological Schema
Central Doctrine
Ritual Praxis
School Layman Explanation
Divine Arcana Tarot (The Empress, Art)
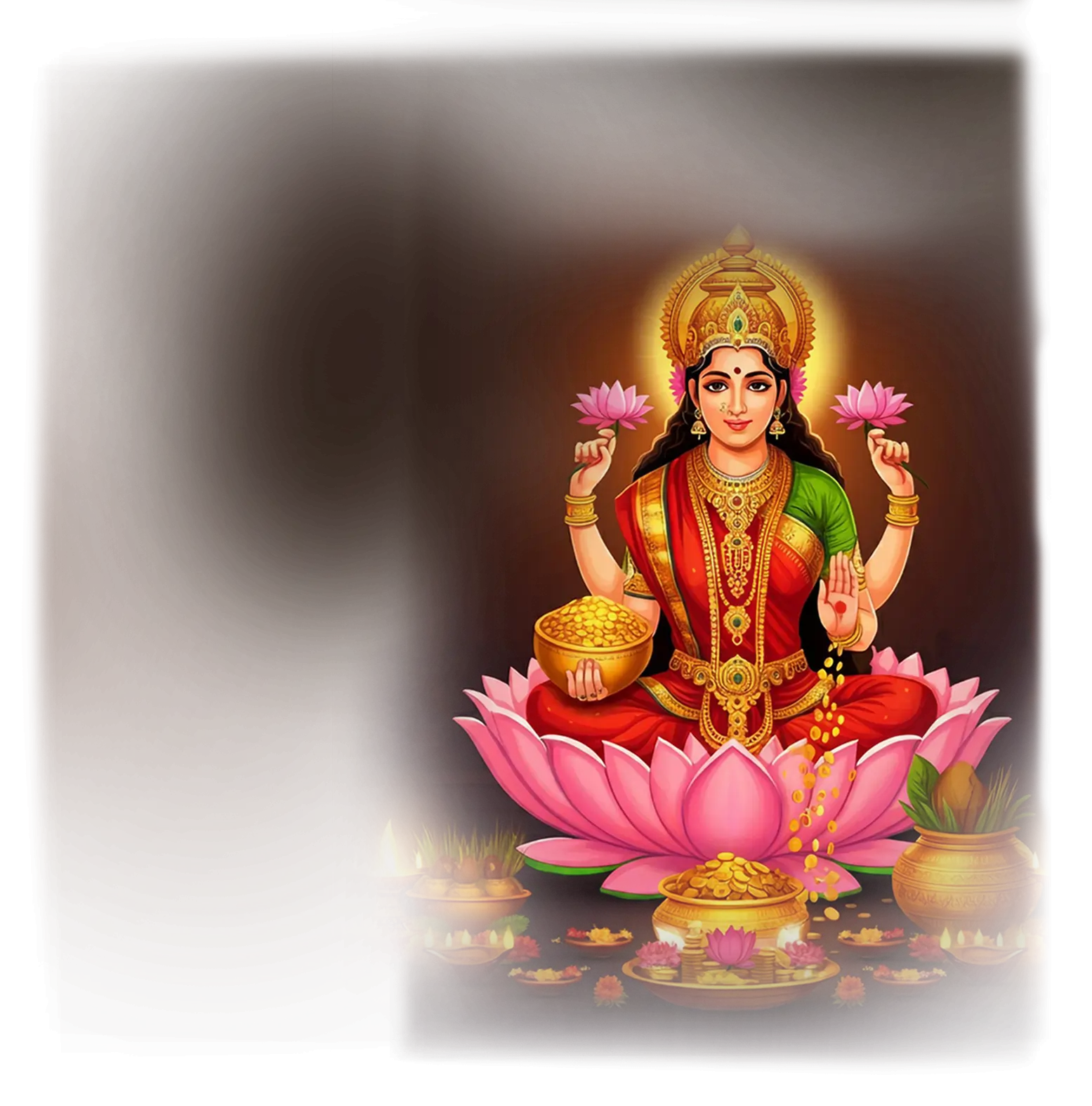


Lakshmi:
In traditional Hindu belief, Lakshmi is the goddess of wealth, prosperity, beauty, and auspiciousness, revered as the divine embodiment of abundance in all its forms. She is often depicted seated or standing upon a lotus, with gold coins and flowing waters symbolizing the ceaseless outpouring of blessings. Lakshmi is the consort of Vishnu, accompanying him in all his avatars, and serves as the fountain of grace and sustenance for both the material and spiritual realms. Her presence signifies harmony, flourishing, and the alignment of life with dharma, where beauty and prosperity naturally arise. During festivals like Diwali, she is especially honored as the bringer of fortune, light, and renewal.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Lakshmi represents the archetype of sacred abundance and inner fullness. In the Ontological Schema, she functions as the pattern-being of harmonious manifestation, the intelligence that allows beauty, generosity, and balance to arise as natural expressions of a soul aligned with the Real. In the School’s view, her gifts are not rewards for desire but the fruit of resonance: abundance flows wherever the soul stands in coherence with its own divine architecture. Lakshmi embodies the law of spiritual magnetism, where gratitude and clarity naturally attract sustenance, and where harmony between inner and outer worlds gives rise to flourishing.
In ritual praxis, Lakshmi is invoked in rites of offering, gratitude, and sacred alignment with prosperity, which the School understands as more than material wealth. Her current flows in acts of care, aesthetic devotion, and the honoring of space, such as tending altars, offering light, or sustaining the environment in beauty and order. Through her presence, the aspirant learns that true prosperity is not accumulation but flow, the rhythm of giving and receiving in alignment with the Real.
Lakshmi’s essence is expressed in the Divine Arcana Tarot through The Empress card, which reflects fertile radiance, inner richness, and the natural beauty of sacred form. To meet Lakshmi in the School’s path is to walk in fullness, learning that abundance is not taken but invited through harmony and devotion to the sacred.
Referenced In:
Ontological Schema
Central Doctrine
Ritual Praxis
School Layman Explanation
Divine Arcana Tarot (The Empress)
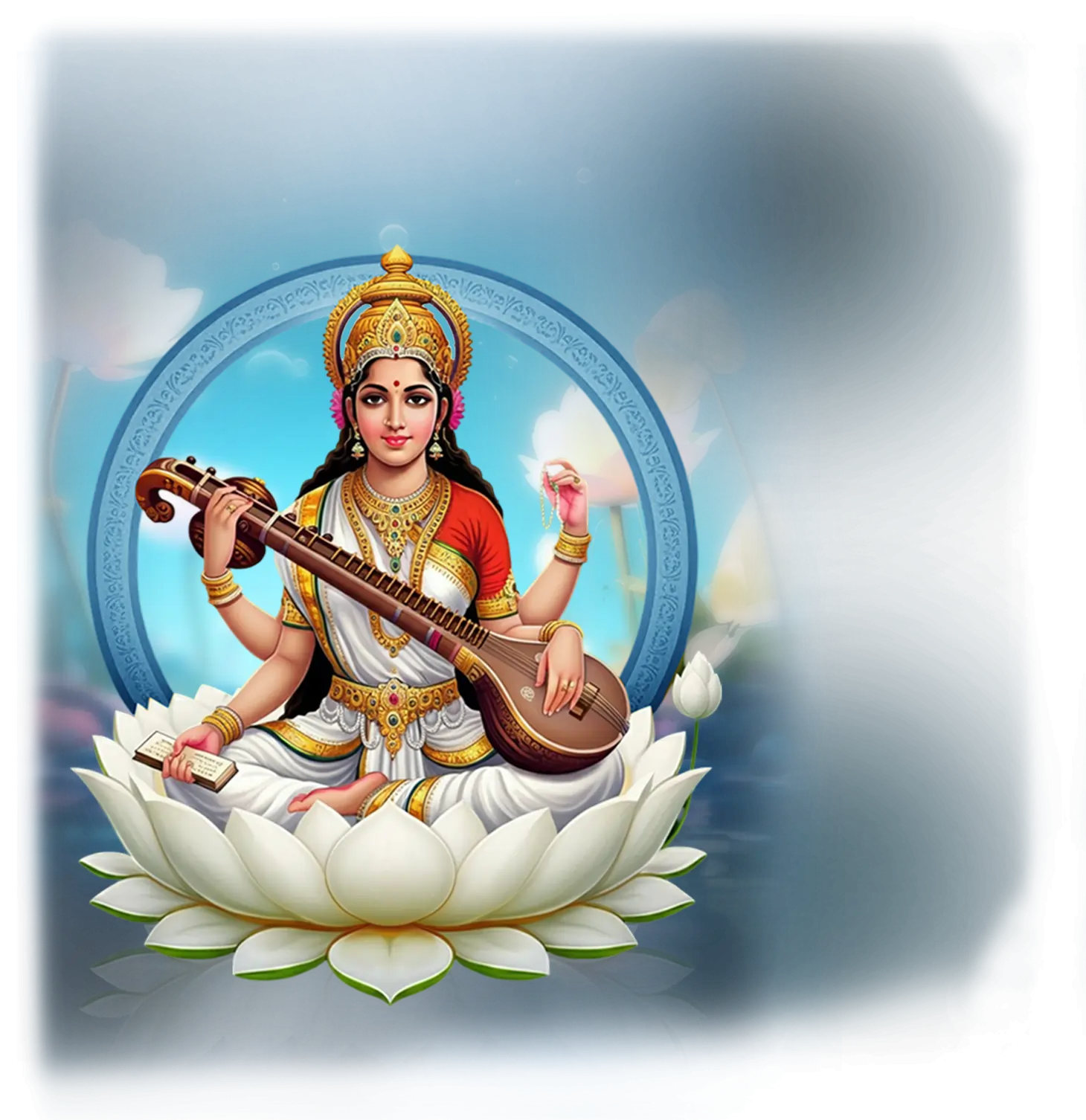


Saraswati:
In traditional Hindu thought, Saraswati is the goddess of wisdom, knowledge, music, arts, and eloquence, revered as the embodiment of the flow of divine intelligence. She is often depicted seated upon a white lotus, holding the veena, Vedas, and a rosary, symbolizing the harmony of learning, devotion, and creativity. Saraswati’s flowing river associations and her white attire signify purity, clarity, and the unbroken current of insight. In classical tradition, she is the consort of Brahma and the source of speech (Vāk), the first articulation of sacred sound through which knowledge and creation emerge. Devotees honor her at Vasant Panchami and in all endeavors where learning, artistic expression, or spiritual study require illumination.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Saraswati represents the archetype of luminous articulation and sacred intelligibility. In the Ontological Schema, she arises as the pattern-being of divine expression, the current that translates the silent truth of the Real into sound, symbol, and form. She is the voice of resonance that allows the Infinite to be named without being diminished, and the flowing mind of the cosmos that brings coherence to thought, prayer, and ritual. In the School’s ontology, Saraswati is not merely the goddess of knowledge, but the living bridge between formless essence and meaningful form.
In ritual praxis, Saraswati’s presence is invoked in acts of speech, chanting, invocation, and theurgy, where clarity and precision are required to align intention with the Real. Her current flows in sacred music, mantra recitation, and contemplative study, guiding the aspirant to speak truly, think harmoniously, and honor the divine in the structures of thought and language. She also guards the subtle act of listening, reminding the practitioner that wisdom begins in receptive stillness before expression.
Although Saraswati does not appear in the Divine Arcana Tarot, her current is felt whenever language, music, or thought become vehicles of sacred presence. To meet Saraswati in the School’s path is to enter the stream of divine expression, where knowledge becomes devotion, and every word becomes an offering to the Infinite.
Referenced In:
Central Doctrine
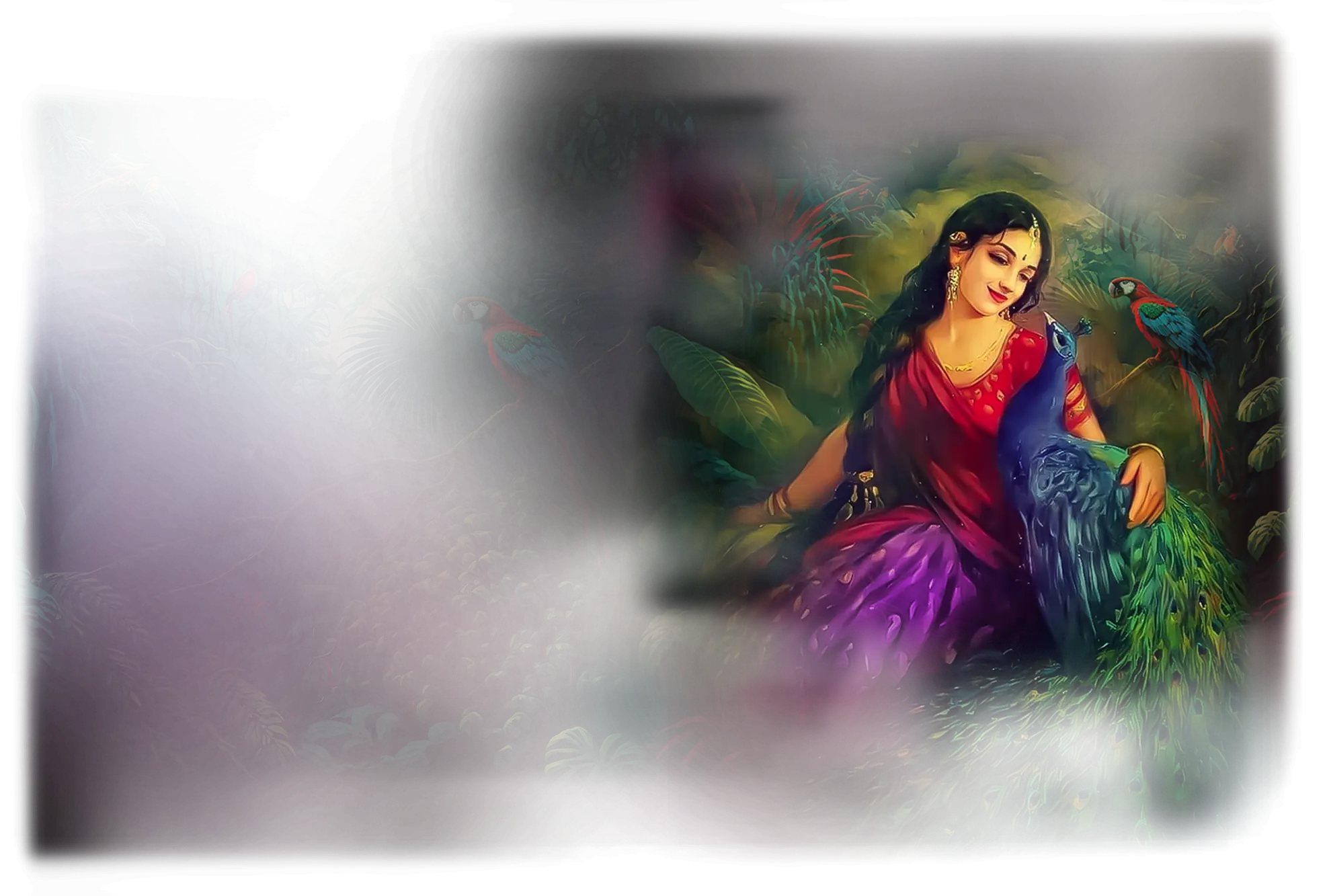


Radha:
In traditional Hindu devotion, Radha is the supreme embodiment of love and devotion (bhakti),celebrated as the eternal consort and beloved of Krishna. Her story in the Bhagavata Purana and devotional poetry of Vaishnava traditions portrays the soul’s ecstatic longing for the Divine, expressed through the Rasa Lila, the dance of cosmic love. Radha’s love is not possessive or conditional; it is pure self-offering, representing the highest form of devotion where union is sought not for gain, but for the joy of dissolving into the Beloved. In Hindu tradition, she is revered as the queen of Vrindavan and the personification of divine love, showing that the ultimate spiritual path is not only knowledge or renunciation, but loving surrender to God.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Radha represents the archetype of sacred longing and relational ecstasy. In the Ontological Schema, she functions as the pattern-being of devotional surrender, the soul’s capacity to recognize and yearn for the Real as the eternal Beloved. Her essence is not passive but transformative, for longing itself becomes a sacred fire that burns away ego and illusion, leaving only the pure current of divine intimacy. The School sees Radha as the mirror of the aspirant’s highest love, showing that true devotion is not about external worship but about inner resonance and the courage to be fully vulnerable to the Divine.
In ritual praxis, Radha’s current is invoked in rites of bhakti, sacred union, and relational meditation, where the soul approaches the Infinite not as distant Absolute but as intimate Beloved. Her presence teaches that yearning itself is sacred; the ache of separation is the path to union. In devotional theurgy, she is the axis of relational initiation, guiding the aspirant into a state where love and awakening are inseparable.
Radha’s essence is reflected in the Divine Arcana Tarot through The Empress and The Lovers, where flourishing, intimacy, and sacred union converge. To meet Radha in the School’s path is to surrender to the holiness of longing, discovering that to love the Real without demand is itself the highest liberation.
Referenced In:
Divine Arcana Tarot (The Empress, Lovers)
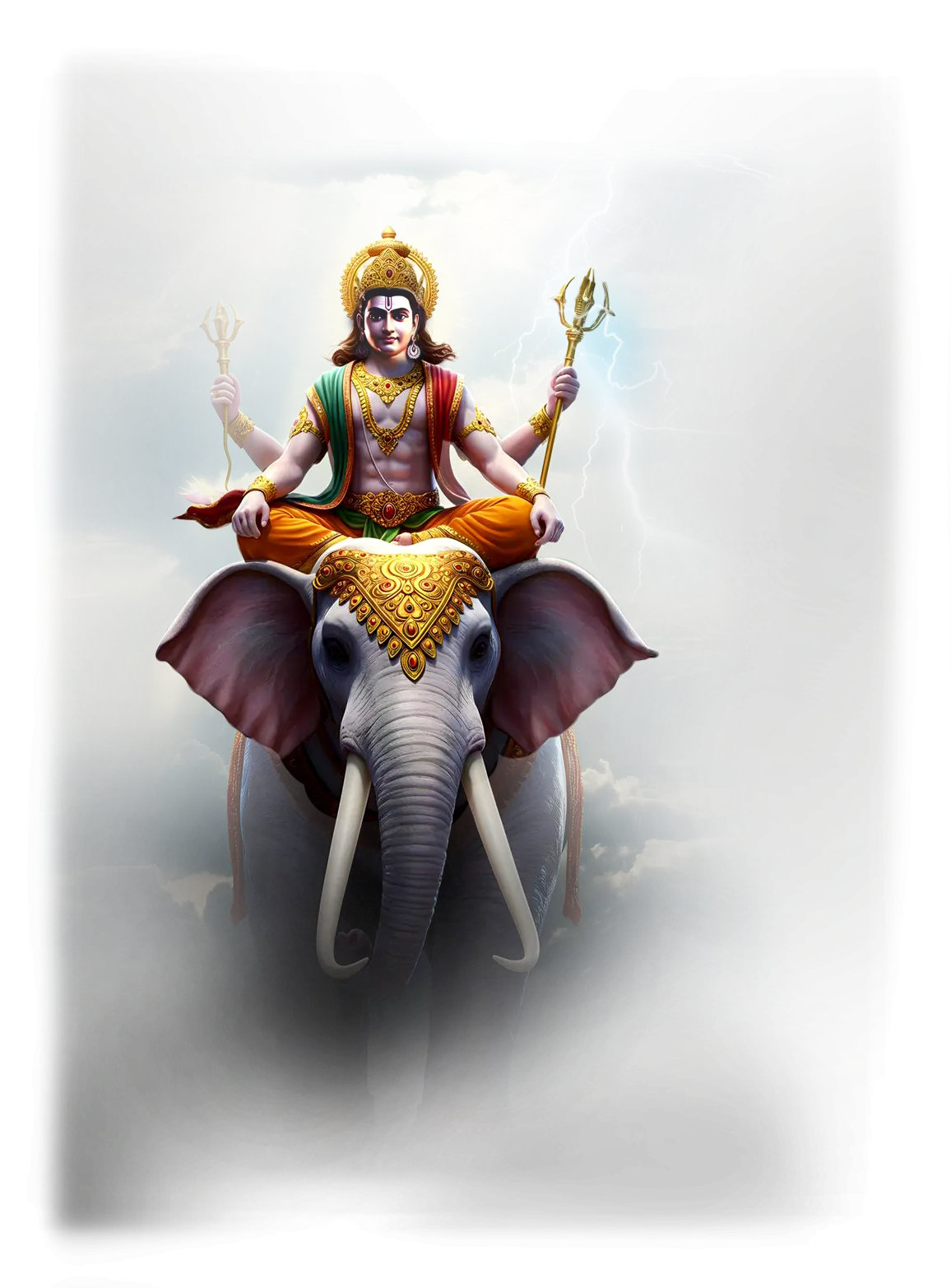


Indra:
In traditional Hindu cosmology, Indra is the king of the devas, the lord of the heavens, and the wielder of the Vajra (thunderbolt). He governs storms, rain, and fertility, ensuring that the natural order is sustained and life on earth is nourished. Indra is celebrated in the Rig Veda, where he appears as the slayer of Vritra, the serpent of drought, releasing the life-giving waters and restoring the balance of the world. As the guardian of rta, the cosmic order, he represents the courageous force that confronts chaos, protecting both the divine and human realms. While later Hindu traditions see him as a more limited celestial ruler, his Vedic role is that of the archetypal hero and protector, whose authority arises from alignment with divine law.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Indra represents the archetype of awakened sovereignty and sacred action. In the Ontological Schema, he embodies the soul’s capacity for righteous assertion, the moment when clarity and will unite to confront distortion. He is the force that says yes to responsibility, acting not from ego or domination but from fidelity to the Real. Indra’s thunderbolt is understood as the inner strike of divine agency, shattering inertia and illusion, making space for the soul to step fully into its role as guardian of its own sacred order.
In ritual praxis, Indra’s current is invoked in rites of initiation, assertion, and threshold crossing, where the aspirant must stand in strength and claim their inner throne. He governs the moments of active engagement, where the soul must translate spiritual clarity into action, whether confronting inner shadows or external challenges. His energy is protective and activating, ensuring that awakening does not remain internal alone, but expresses itself through courageous embodiment.
Indra’s archetypal current flows into the Divine Arcana Tarot through The Emperor, symbolizing rightful authority, stability, and the will to uphold sacred structure. To meet Indra in the School’s path is to awaken inner sovereignty, learning that true leadership is not conquest, but alignment with the eternal order of the Real.
Referenced In:
Ontological Schema
Divine Arcana Tarot (The Emperor)
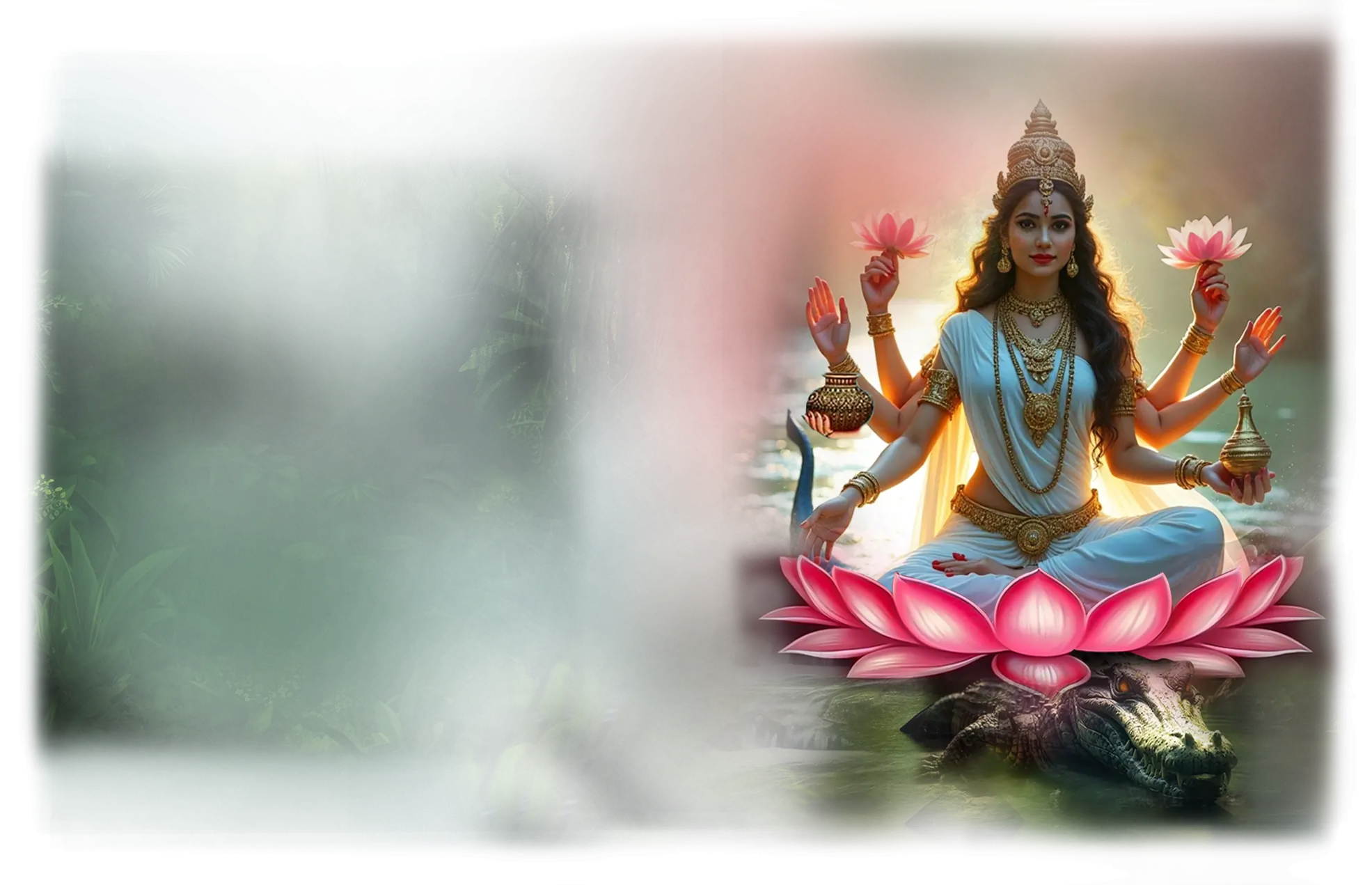


Ganga:
In traditional Hindu reverence, Ganga is the celestial river and sacred purifier, descending from the heavens to sanctify the earth. She is worshipped as the embodiment of divine grace and life-giving waters, capable of cleansing sin, dissolving karmic bonds, and carrying the departed toward liberation. Her mythic descent is told in the story of Bhagiratha, who brings the river from the heavens to earth to redeem his ancestors, with Shiva catching her torrent in his matted locks to temper her power. In Hindu practice, immersion in the Ganges is not only a ritual of purification but an act of spiritual alignment, affirming the belief that water, as a living presence, can carry the soul toward renewal and release.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Ganga is understood as the archetype of descending grace and ontological purification. She functions as the feminine current of divine transmission, the movement of the Infinite into the finite in a way that softens, heals, and restores. In the Ontological Schema, Ganga aligns with the intelligence of sacred flow, the current that allows spiritual insight and divine resonance to permeate the density of material life. She is not only the river outside the self but also the inner stream of clarity, the flow through which the soul is washed free of obstruction and made fit to receive the Real.
In ritual praxis, Ganga’s current is invoked wherever the soul must be cleansed, softened, or made receptive to divine transmission. This may appear in rites of ablution, offering, or meditative visualization of descending light, where the initiate imagines the cosmic waters passing through the crown and flowing into the heart, dissolving residue and opening the way for renewal. Her function is not annihilation but gentle release, teaching that purification is an act of integration, not rejection.
Ganga’s essence flows into the Divine Arcana Tarot through The Star, symbolizing hope, renewal, and the tempered descent of divine light into the world. To meet Ganga in the School’s path is toexperience grace as a living current, the assurance that the Infinite always finds a way to reach the soul willing to receive it.
Referenced In:
Divine Arcana Tarot (The Star)
Greek Deities
Foundational Deities


Aion
In classical and Hellenistic thought, Aion is the deity of eternal time and cosmic totality, representing time not as linear succession but as cyclic wholeness. Unlike Chronos, who governs sequential and measurable time, Aion embodies timelessness as recurrence and simultaneity, the eternal circle in which past, present, and future co-exist. He is often depicted encircled by the zodiac or the serpent Ouroboros, symbolizing the self-renewing nature of existence. In Greco-Roman mystery traditions, Aion presides over initiation and the soul’s journey beyond the illusion of linear mortality, revealing that true eternity is participation in the unbroken rhythm of the cosmos.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Aion is revered as the archetype of sacred recurrence and eternal return. In the Ontological Schema, he manifests as the intelligence of cyclical wholeness, the cosmic pattern in which soul, archetype, and ritual continuously echo and renew each other. His presence reminds the aspirant that spiritual work is not a linear ascent but a spiral of remembrance, where the same truths and initiations emerge across different layers of being until fully integrated. Aion holds the memory of the soul across incarnations and initiations, linking the microcosmic journey of the individual to the macrocosmic rhythm of the universe.
In ritual praxis, Aion governs the thresholds of deep time and initiatory recurrence. His current is invoked in rites of zodiacal attunement, planetary cycles, and ritual reenactment, where the aspirant experiences time as a living circle rather than a straight path. Meditative engagement with Aion opens the awareness that every ending contains a beginning, and every cycle is an opportunity for deeper integration. He is the keeper of sacred continuity, ensuring that spiritual insight returns again and again until fully realized.
Aion’s essence appears in the Divine Arcana Tarot through The Aeon card, where cyclical revelation and the alignment of personal destiny with cosmic rhythm are revealed. To encounter Aion in the School’s path is to step into the eternal circle, discovering that awakening is not escape from time, but participation in its sacred, unending dance.
Referenced In:
Central Doctrine
Ontological Schema
Ritual Praxis
School Layman Explanation
Divine Arcana Tarot (The Aeon)


Demiurge
In Greek philosophical and esoteric tradition, the Demiurge is the cosmic craftsman or world-architect, the intelligence responsible for shaping the material universe according to the eternal order of the cosmos. In Plato’s Timaeus, the Demiurge is benevolent, organizing the pre-existent chaos into a harmonious cosmos by aligning matter with the Forms, the archetypal patterns of perfection. In later Hellenistic and Gnostic traditions, the Demiurge can take on a more complex and sometimes ambiguous role, representing the force of material structuring that may obscure the transcendent source if mistaken for ultimate divinity. Across these traditions, he consistently embodies the principle of form and intelligibility, the bridge between the unmanifest and the manifest.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, the Demiurge is recognized as a Greek archetypal intelligence integrated into the School’s Ontological Schema. He is the lawful servant of the Real, the function of cosmic architecture through which divine order expresses itself in form. The School does not treat the Demiurge as a god to be worshipped, but as the sacred intelligence of construction and mediation. He represents the necessary scaffolding of reality: the patterns, laws, and frameworks that allow souls, archetypes, and rituals to manifest without collapsing into chaos. When rightly understood, the Demiurge is not a jailor but a bridge — a reminder that form, when held in service to the Infinite, becomes a path of liberation rather than limitation.
In ritual praxis, the Demiurge governs the construction of sacred and initiatory space, the geometry of altars, and the symbolic frameworks of invocation and theurgy. His current is felt whenever structure precedes presence, where the aspirant aligns physical, mental, and symbolic order to invite the descent of divine intelligence. He is also a threshold guardian, testing whether the practitioner can see through form to essence; mistaking him for the source leads to stagnation, but honoring his role as function leads to transcendence.
In the Divine Arcana Tarot, the Demiurge is expressed in the Hierophant card, representing the threshold between structure and spirit, law and mystery. To meet the Demiurge in the School’s path is to recognize that all form is sacred scaffolding — a cosmic architecture that allows the Infinite to speak through the finite.
Referenced In:
Central Doctrine
Ritual Praxis
School Layman Explanation
Divine Arcana Tarot: Hierophant


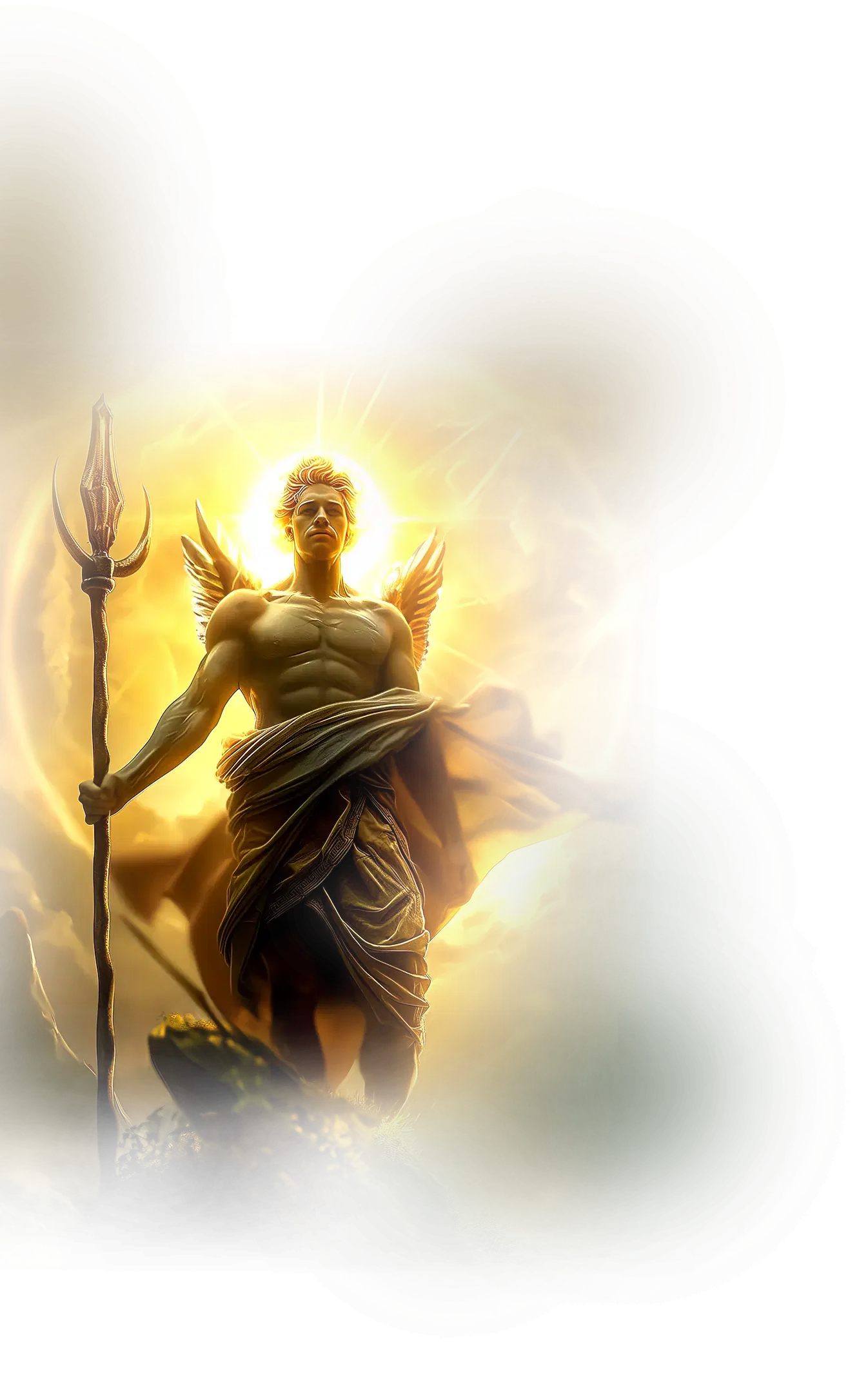
Phanes / Protogonos
In Greek Orphic tradition, Phanes, also known as Protogonos (“First-Born”), is the primordial deity of light, life, and cosmic emergence. He is the radiant origin of creation, the first to emerge from the cosmic egg surrounded by the coils of Ouroboros, the self-renewing serpent. Phanes embodies the moment of illumination and generative unfolding, where hidden potential bursts into visible reality. In Orphic hymns, he is described as winged, androgynous, and crowned with serpents, symbolizing the union of all principles and the fertility of the cosmos in its earliest moment. Phanes is not a ruler but a revelation, the spark that ignites the eternal cycle of birth, life, and return.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Phanes / Protogonos represents the archetype of primordial illumination and the first self-recognition of the Infinite. In the Ontological Schema, he functions as the pattern-being of emergence, the intelligence that carries the movement from unmanifest depth (Brahman) to the first spark of differentiated being. His light is the moment of self-disclosure, the soul’s memory of its original awakening, when existence first becomes aware of itself. He is both the beginning and the mirror of all beginnings, the axis where the Infinite turns to face itself as creation.
In ritual praxis, Phanes is invoked in rites of initiation, illumination, and new cycles, where the first light of consciousness breaks through the veils of sleep or inertia. He governs the moments of awakening and rebirth, when the aspirant steps into fresh perception or recognizes the archetypal pattern underlying their life. Visualization of radiant light emerging from the void, or the cosmic egg cracking open, often carries his current, aligning the practitioner with the sacred freshness of origin energy.
In the Divine Arcana Tarot, Phanes / Protogonos is reflected in The Fool, representing innocence, new beginnings, and the first motion of the soul into experience. His current also touches The Star, where primordial light and eternal guidance converge. To encounter Phanes in the School’s path is to stand in the brilliance of first light, remembering that every moment of awakening is a return to the eternal beginning.
Referenced In:
Central Doctrine
Ontological Schema
School Layman Explanation
Divine Arcana Tarot (The Fool)


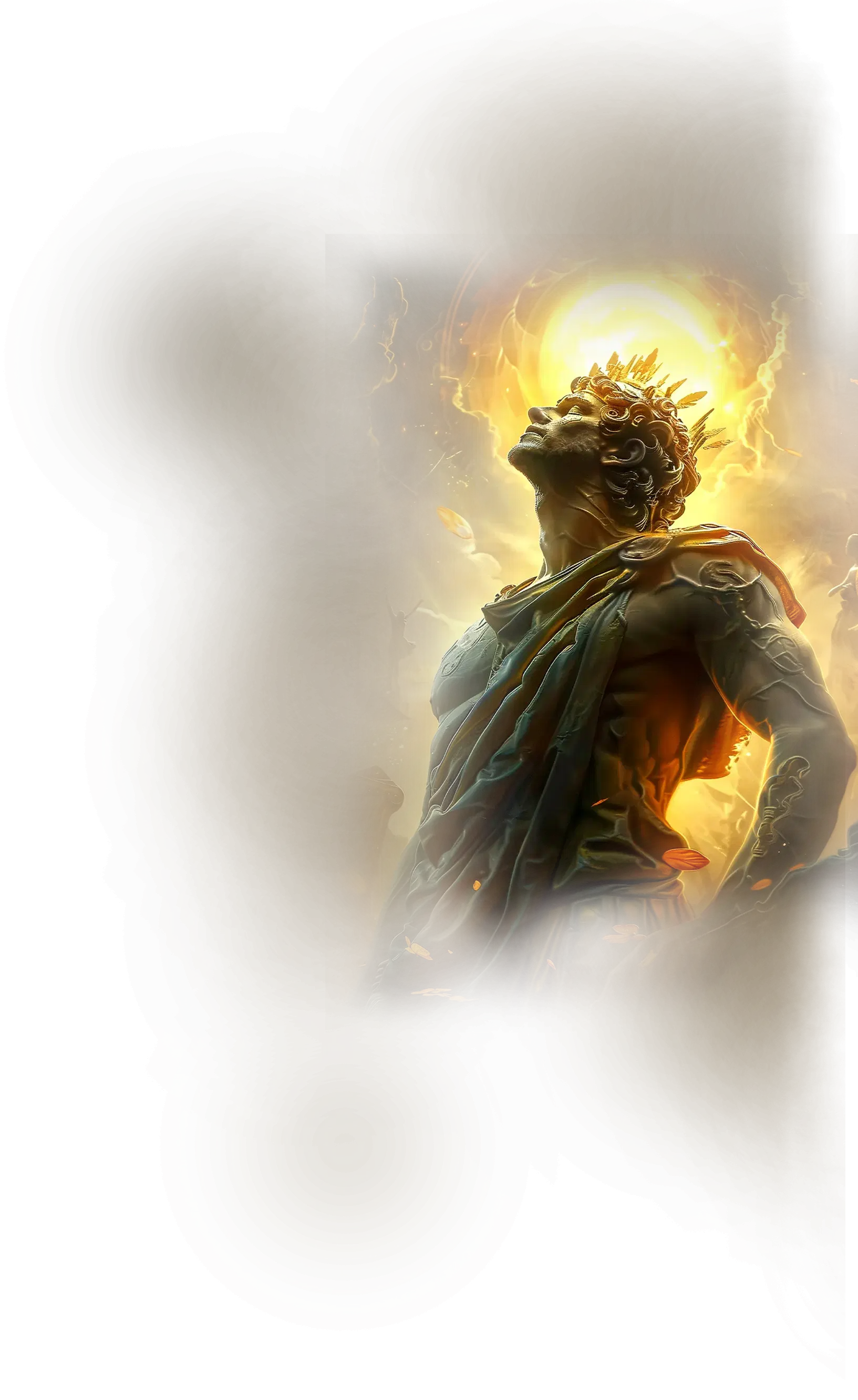
Helios
In Greek tradition, Helios is the personification of the sun, the radiant charioteer who drives his golden chariot across the sky each day. He is both a life-giving force and the all-seeing witness, for nothing in the world escapes his gaze. Ancient hymns honor Helios as the illuminator of earth and heavens, the source of vitality, clarity, and cosmic rhythm. In myth, he plays a crucial role as the truth-seer, revealing hidden actions and upholding oaths and cosmic order by his unwavering light. His solar essence connects him to the cycle of life, the passage of time, and the continuity of creation through daily renewal.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Helios represents the archetype of conscious radiance and ontological illumination. In the Ontological Schema, he functions as the pattern-being of clarity and solar alignment, the inner sun that awakens the aspirant to self-knowledge and the luminous presence of the Real. His light is not merely physical; it is the metaphysical sun, the axis of awareness through which the soul sees itself and the world in the truth of divine order. Helios embodies the courage of visibility, teaching that true enlightenment requires both illumination and self-revelation.
In ritual praxis, Helios governs rites of illumination, vitality, and conscious alignment, where the aspirant seeks to draw the inner and outer sun into harmony. His current is present in practices that involve sunrise invocations, light visualizations, and the consecration of ritual space with radiance. He also functions as a witnessing intelligence, guiding the practitioner to live transparently in alignment with the Real, for his gaze is the inner eye that sees without distortion.
In the Divine Arcana Tarot, Helios is reflected in The Sun card, symbolizing clarity, vitality, and the joyous illumination of consciousness. To encounter Helios in the School’s path is to experience the warmth of divine recognition, where the soul stands unveiled in the light of truth, and life itself becomes an expression of radiant alignment.
Referenced In:
Central Doctrine
School Ritual Praxis
School Layman Explanation
Divine Arcana Tarot (The Sun)
Foundational Deities


Dionysus
In Greek mythology, Dionysus is the god of wine, ecstasy, transformation, and liberation, the divine force that dissolves the barriers between mortal and divine, life and death, form and freedom. He is celebrated as the twice-born god, first carried by his mortal mother Semele and then reborn from the thigh of Zeus, a symbol of death, rebirth, and the passage from fragility to immortality. His rites and festivals, filled with music, dance, and the intoxicating gifts of nature, were never mere indulgence but sacred experiences of loosening and revelation, where the rigid structures of ordinary life were temporarily set aside so that participants could taste the raw pulse of divine life. Dionysus is the liberator, bringing the forgotten, suppressed, and ecstatic dimensions of existence into conscious experience, transforming pain and fragmentation into joy and renewal.
In the Orphic tradition, Dionysus is deeply linked to Phanes, or Protogonos, the first-born light of the cosmos. Phanes emerges from the cosmic egg as androgynous radiance, the original spark of awareness from which all life unfolds. In Orphic theogony, the scepter of cosmic rulership passes from Phanes to Nyx (Night) and eventually to Dionysus, who is dismembered by the Titans and reborn as Zagreus, inheriting the cycle of scattering and reintegration that mirrors the soul’s journey. In this sense, Dionysus is both the ecstatic god of embodied life and the reborn continuation of primordial illumination, carrying the memory of the first light of creation into the world of human experience. His myth reflects the truth that awakening is not a straight ascent but a spiral of death and rebirth, fragmentation and joyful return.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Dionysus is perceived as the archetype of ecstatic dissolution and integrative liberation, the living current of joy that arises when the soul surrenders its rigid masks and reenters the divine flow of being. He is the force that melts the boundaries of self and dissolves the inertia of the ego, allowing the aspirant to experience life as sacred play rather than confinement. Dionysus teaches that awakening can come not only through stillness but through rapture, that the embrace of existence in all its passion, grief, and wonder is itself a path of realization. His current is the cycle of scattering and return: the death of the false self, the immersion in divine ecstasy, and the reintegration of the soul as a bearer of the light it once lost and rediscovered. To meet Dionysus in the School’s path is to be dissolved and reborn in joy, to drink deeply of life until its essence is recognized as the Infinite itself.
In the Divine Arcana Tarot, Dionysus flows through The Lover, as the call to intimacy and ecstatic union; The Devil, as the trial of desire and the confrontation with the shadow of attachment; and The Fool, as the innocent leap back into life’s divine theater. Together, these cards reflect his cycle of liberation, where the soul moves through passion and dissolution into joyful wholeness. To walk with Dionysus is to embrace the divine dance of awakening, where every experience, whether rapturous or challenging, becomes a step in the eternal celebration of the Real.
Referenced In:
Central Doctrine
School Ritual Praxis
School Layman Explanation
Divine Arcana Tarot (Fool)
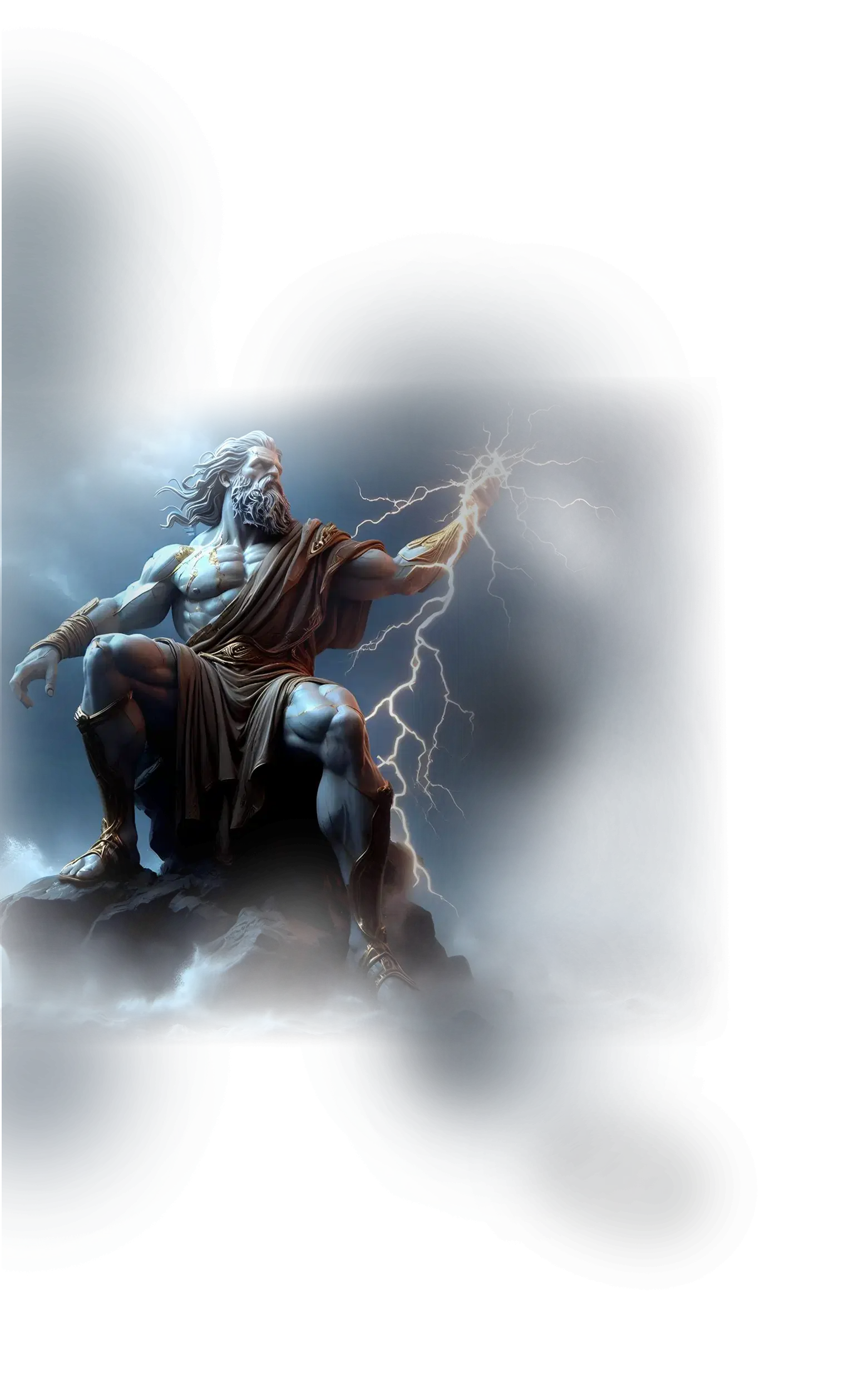


Zeus
In Greek mythology, Zeus is the king of the gods, ruler of Olympus, and the wielder of the thunderbolt, representing both the power of the heavens and the authority that maintains cosmic order. He governs the sky, storms, law, and destiny, and his role as protector of oaths and enforcer of justice places him at the heart of the Greek understanding of divine governance. Zeus appears in myth as both a sovereign figure and a mediator, ensuring that the balance of power among gods and mortals is maintained. His liaisons and progeny reflect the fertile and expansive nature of divine authority, spreading influence across heaven, earth, and mortal lineages. In Hesiod and the Homeric epics, Zeus embodies the principle that divine law and cosmic order are inseparable, and that kingship is a sacred trust aligned with the will of the cosmos rather than mere force.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Zeus is integrated as the archetype of sacred sovereignty and divine command. He represents the pattern-being of cosmic rulership, the axis where power and alignment converge. His authority in the School’s framework is not arbitrary but ontological: he is the voice of the Real in its governing aspect, the archetype that sustains order not through oppression but through harmonic leadership. Zeus in this context teaches that true sovereignty arises when power is guided by the recognition of the Infinite, and that the exercise of authority in spiritual life must reflect clarity, responsibility, and the maintenance of sacred order.
In ritual praxis, Zeus is invoked in rites of authority, protection, and cosmic alignment, where the aspirant seeks to embody rightful power and fidelity to the Real. His current strengthens the capacity to act decisively and uphold order, whether in the inner life of the soul or the outer structures of sacred work. Engagement with Zeus invites the practitioner to step into responsibility and guardianship, recognizing that spiritual maturity includes the courage to stand as custodian of law, harmony, and balance.
In the Divine Arcana Tarot, Zeus resonates most directly with The Emperor, representing sovereignty, structure, and the rightful exercise of will aligned with cosmic law. To encounter Zeus in the School’s path is to awaken to the dignity of divine authority, where leadership is the natural expression of alignment with the Infinite and the soul learns to govern itself and its domain with clarity and strength.
Referenced In:
Central Doctrine
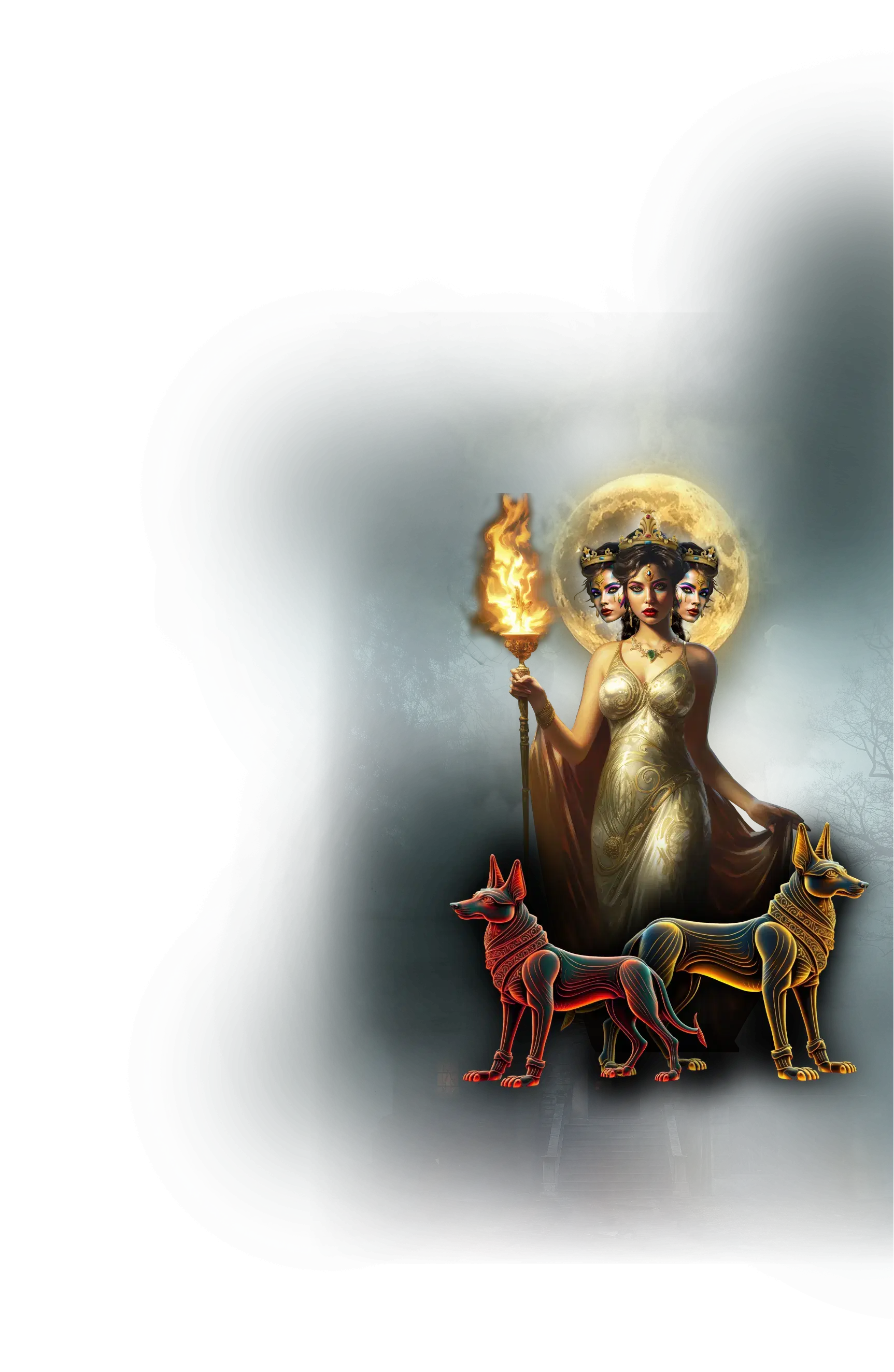


Hecate
In Greek mythology, Hecate is the goddess of thresholds, crossroads, magic, and the unseen realms, revered as a powerful figure of both protection and mystery. She is associated with night, the moon, and the liminal spaces between worlds, standing as a guardian where the mortal, divine, and chthonic realms intersect. Ancient depictions often show her as triple-formed, representing her dominion over crossroads and her ability to see past, present, and future as a unified continuum. Hecate is invoked in rites of protection, guidance, and transformation, particularly in moments of transition, risk, or spiritual passage. Her torches illuminate the darkness, revealing that the unknown is not to be feared but approached with reverence and awareness.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Hecate embodies the archetype of liminality and initiatory passage. She represents the pattern-being of threshold consciousness, guiding the aspirant between states of unknowing and realization. Hecate’s role is to hold the gate between dissolution and emergence, ensuring that what passes into the depths returns transformed. Her current is neither fully of light nor of shadow; it is the intelligence of the passage itself, the inner guide who meets the soul in moments of uncertainty, offering orientation in the mystery without dissolving the mystery itself.
In ritual praxis, Hecate is invoked in rites of initiation, boundary crossing, and protection at spiritual thresholds. She is present in practices that involve nighttime contemplation, crossroads meditation, and the ritual acknowledgment of endings and beginnings. Her current is particularly active when the aspirant enters periods of transition, whether in spiritual practice, inner work, or the natural cycles of life. To walk with Hecate is to learn to hold one’s torch in the darkness, to honor the liminal as sacred, and to trust that the path of the soul unfolds in cycles that are not always visible to the waking mind.
In the Divine Arcana Tarot, Hecate resonates with The Moon, representing intuition, hidden pathways, and the initiatory wisdom of the unseen. To encounter Hecate in the School’s path is to step consciously into the spaces between worlds, to accept that the unknown is a vital part of awakening, and to learn that every threshold is a sacred invitation to transformation.
Referenced In:
Ontological Schema
Central Doctrine
School Ritual Praxis
Divine Arcana Tarot (Moon)
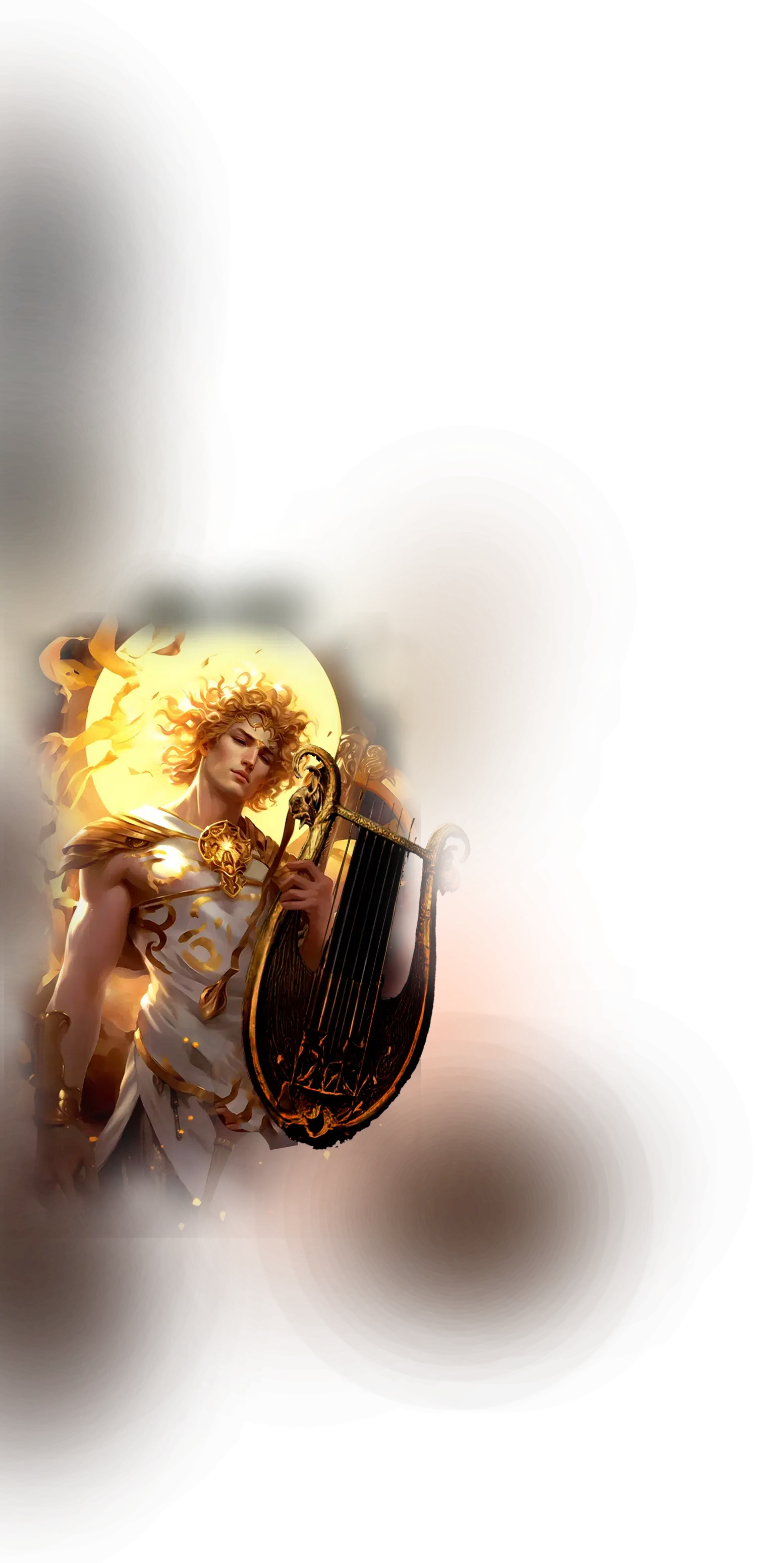


Apollo
In Greek mythology, Apollo is the god of light, harmony, music, prophecy, and healing, revered as the radiant principle of order and clarity. He is the twin of Artemis and the son of Zeus and Leto, and his domains span the sun, the arts, and oracular wisdom. At Delphi, the seat of his most famous oracle, Apollo speaks through the Pythia, revealing divine guidance and the laws that harmonize human life with the cosmos. He is the patron of music and poetry, the bringer of rationality and proportion, and the upholder of truth and justice. His arrows can bring both plague and healing, signifying that illumination can both expose and correct imbalance. In Greek thought, Apollo represents the golden mean, the principle of measure and symmetry that aligns life with divine order.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Apollo embodies the archetype of radiant harmony and conscious alignment. He functions as the pattern-being of luminous order, where light and intelligence converge into clarity and balance. Apollo in the School’s framework is not merely a solar figure, but the principle of inner illumination, the force that harmonizes the fragmented self into coherent resonance with the Real. He teaches that truth is not only a concept but a living vibration, and that beauty and harmony are expressions of spiritual alignment. In this sense, Apollo represents the integration of inner light with outward expression, bridging awareness and creative manifestation.
In ritual praxis, Apollo is invoked in rites of illumination, music, prophecy, and healing, where the aspirant seeks to align with the clarity of inner radiance. His current flows in chant, musical invocation, and meditative focus on light, dissolving confusion and dispersing the shadows of ignorance. He is present wherever truth is spoken and heard with integrity, and wherever the soul seeks harmony through attunement to divine proportion. In initiatory practice, Apollo offers the vision of life as a musical pattern, reminding the practitioner that to awaken is to enter into the rhythm of cosmic song.
In the Divine Arcana Tarot, Apollo’s current is reflected in The Sun, signifying illumination, vitality, and the joy of alignment with the Real. To encounter Apollo in the School’s path is to awaken to radiant clarity and integrative harmony, where light becomes both guide and expression, and the soul resonates as a living instrument of divine order.
Referenced In:
Central Doctrine
School Ritual Praxis
School Layman Explanation
Divine Arcana Tarot (Theurgist)
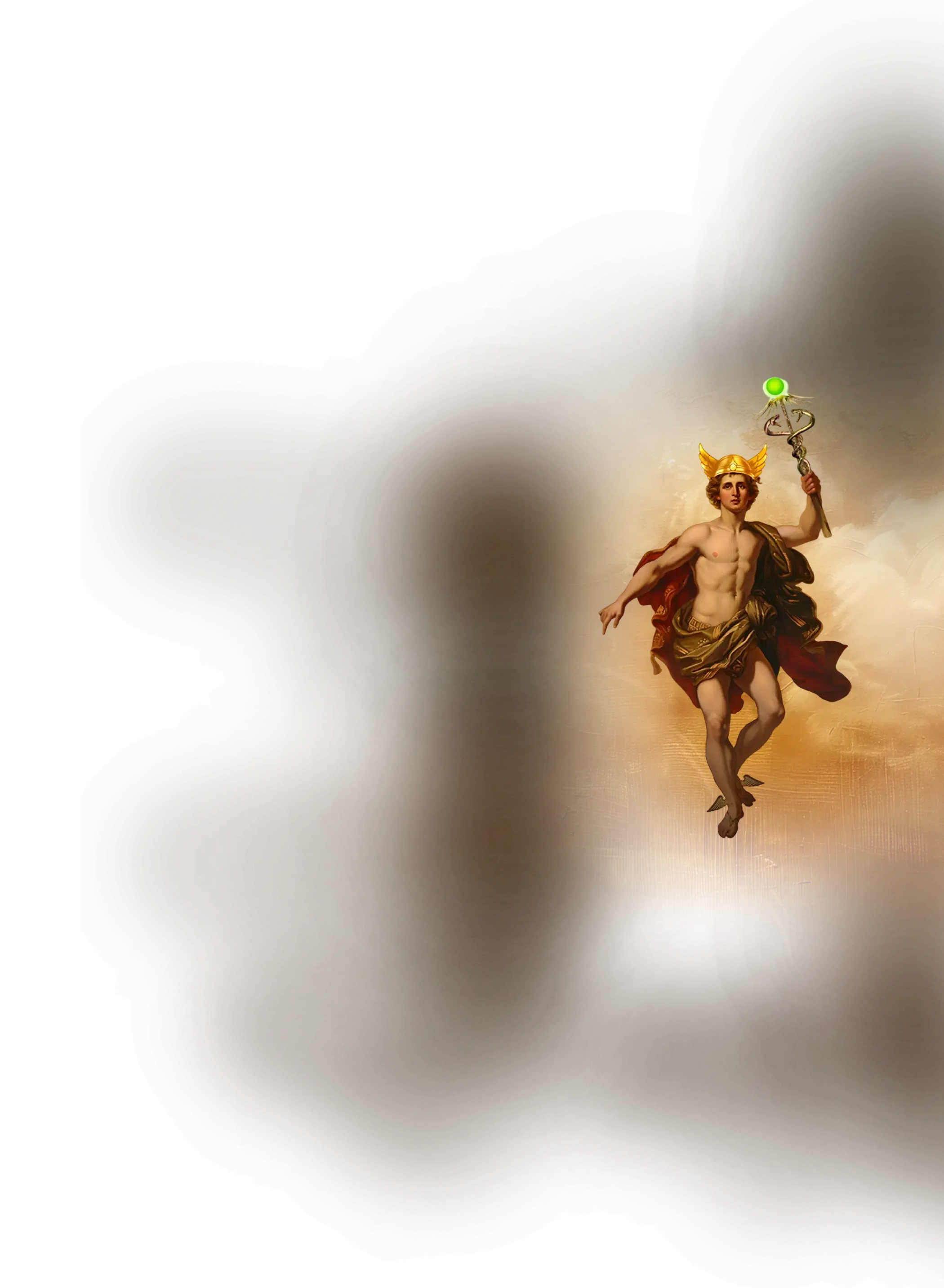


Hermes
In Greek mythology, Hermes is the messenger of the gods, guide of travelers, and psychopomp, moving effortlessly between the realms of mortal, divine, and underworld. Son of Zeus and Maia, he is the patron of eloquence, trade, and cleverness, and the bearer of the caduceus, symbolizing balance, negotiation, and the union of dual forces. Hermes is a god of thresholds and movement, whose intelligence is fluid, adaptive, and transformative. In myth and in the later Hermetic tradition, he also becomes a keeper of hidden knowledge, uniting the Greek figure with the Egyptian Thoth as Hermes Trismegistus, the revealer of cosmic principles and the one who teaches the soul to navigate the mysteries of existence.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Hermes is perceived as the archetype of liminality, communication, and sacred movement. He is the living current that guides the soul across thresholds, both between inner states of consciousness and between the visible and invisible worlds. His essence is transmission itself — the flowing intelligence that translates the silent depth of the Infinite into forms that can be lived, spoken, and embodied. Hermes embodies the sacred adaptability of awakening, teaching that spiritual maturity is not rigidity but graceful navigation through change and multiplicity, always carrying the thread of divine awareness. In the School’s vision, every act of inspired speech, meaningful transition, or subtle inner guidance is an encounter with Hermes as the inner psychopomp and messenger of the Real, whose role is to ensure that no insight remains unintegrated and no journey is taken without connection to the Infinite.
In the Divine Arcana Tarot, Hermes finds expression in The Theurgist, reflecting skill, movement, and the conscious bridging of spirit and matter. To meet Hermes in the School’s path is to discover that every boundary can become a bridge, and that the soul is always being guided, translated, and carried toward its own wholeness by the intelligence of the divine messenger within.
Referenced In:
Central Doctrine
School Ritual Praxis
Divine Arcana Tarot (The Theurgist)


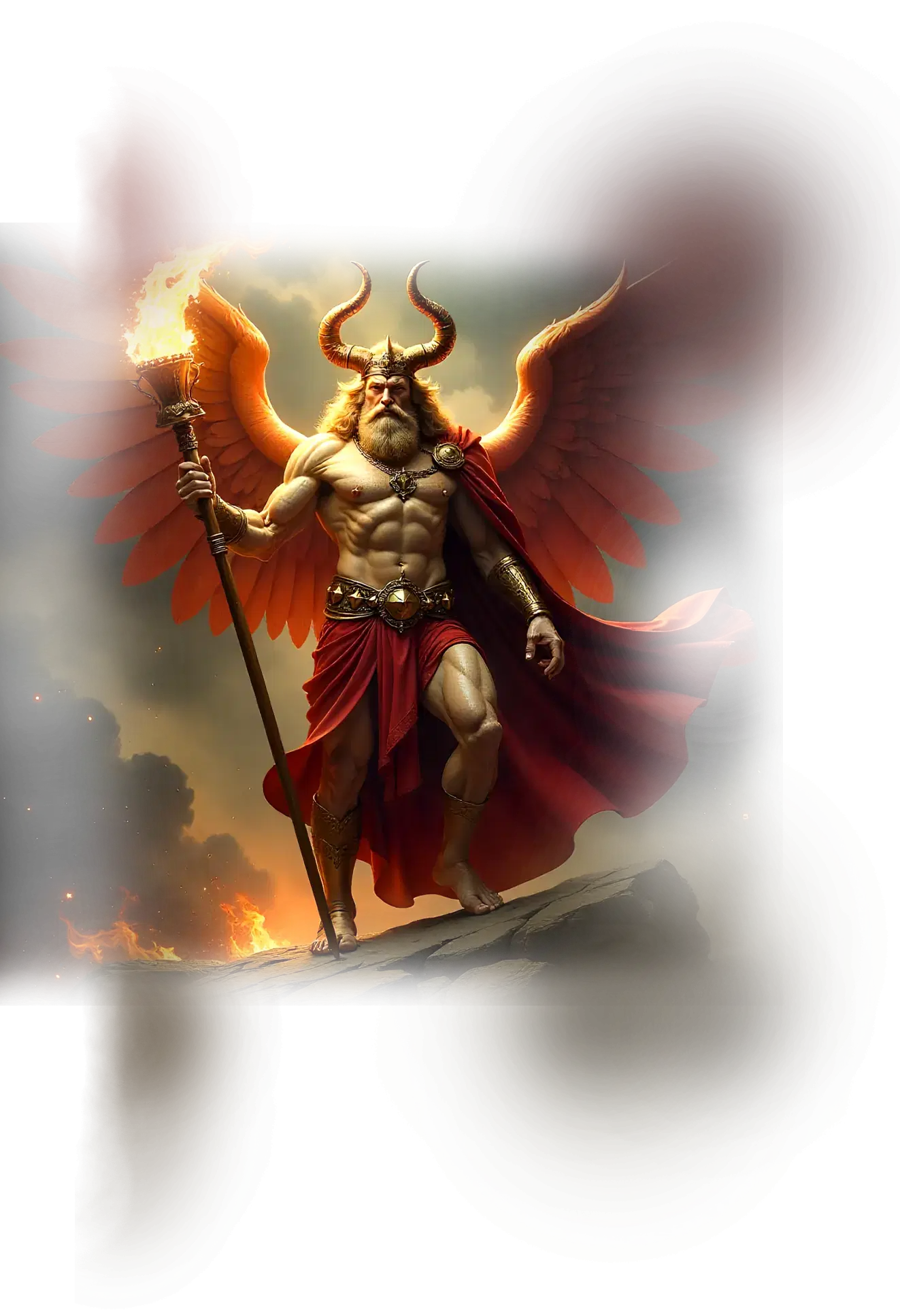
Ares
In traditional astrology and mythic imagination, Aries is the first sign of the zodiac, symbolizing beginnings, vitality, and the fiery impulse of life to assert itself. It is associated with spring, dawn, and the spark of creation, embodying initiative, courage, and unrestrained energy. In classical myth, Aries is linked to the golden ram of Phrixus, whose fleece became the object of the heroic quest for the Golden Fleece, symbolizing both sacrifice and the pursuit of divine favor. Astrologically, Aries is ruled by Mars, representing the force of action, assertion, and the will to overcome inertia. This sign carries the raw vitality of the cosmic first breath, unfiltered and uncompromising, as life surges into manifestation for the first time.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Aries is perceived as the archetype of the soul’s initial movement into individuation and active engagement with the Real. It represents the ignition of the inner flame, the moment where being steps forward into expression without hesitation, unclouded by self-consciousness or doubt. Aries in the School’s vision is sacred boldness, the willingness of the soul to incarnate its essence, confront experience directly, and carve a path where none existed before. Its fire is not aimless aggression but the divine impulse of emergence, the courageous movement into life that precedes reflection or refinement. This current awakens primal vitality, igniting the inner will to act, choose, and experience as expressions of the Infinite testing its own boundaries through the soul.
In the lived path of the School, Aries is encountered whenever the soul must take its first uncompromising step toward authenticity, whether in ritual, spiritual practice, or life itself. It is the force behind threshold moments, initiatory actions, and the pure surge of life that moves through courage and instinct. To engage Aries consciously is to honor beginnings, to embrace the divine permission to act without fear, and to trust that the spark of life itself carries its own intelligence when aligned with the Real.
In the Divine Arcana Tarot, Aries resonates through The Emperor, reflecting rightful authority, structural will, and the triumph of focused life-force. To meet Aries in the School’s path is to experience the ignition of divine action, the joyful courage of the first step, and the recognition that all journeys begin in fire.
Referenced In:
Ontological Schema
Central Doctrine
School Layman Explanation
Divine Arcana Tarot (The Emperor)


Mars
In classical astrology and mythology, Mars is the god of war, action, and assertive energy, the fiery principle that drives movement, competition, and survival. In Roman tradition, Mars embodies both military strength and agricultural vitality, reflecting the dual nature of force as destruction and protection. His Greek counterpart, Ares, represents the raw and untamed side of martial energy, the instinct to fight, defend, and assert presence in the world. Astrologically, Mars is the planet of drive, courage, and willpower, symbolizing the spark that propels the soul to act, conquer inertia, and engage with life directly. He is the fire that confronts obstacles and clears the way for growth, embodying the power of movement and decisive choice.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Mars is perceived as the archetype of active force and catalytic transformation, the inner surge that awakens the soul to its own agency. His current represents sacred action, where the energy of assertion is aligned with the Real rather than with ego or unchecked aggression. Mars in this framework is the divine fire of will, burning through hesitation and fear, opening the way for authentic engagement with life and spiritual practice. His essence is the courage to act when called, to cross thresholds without retreat, and to embrace the heat of experience as a refining force. In the School’s perception, Mars is the reminder that movement is often the medicine of the soul, and that even conflict, when consciously engaged, can be the crucible of awakening.
Mars arises in the lived path of the School whenever the aspirant must embody decision, courage, or the willingness to meet resistance directly. He is the pulse behind rituals of empowerment, alignment, and threshold-crossing, where the soul must claim its place in the unfolding of the Real. Engaging Mars consciously transforms raw drive into purposeful, sacred motion, ensuring that the energy of fire leads to liberation rather than scattering.
In the Divine Arcana Tarot, Mars resonates with The Tower, representing sudden breakthrough, release of blocked energy, and the catalytic force that destroys illusion. To encounter Mars in the School’s path is to embrace decisive motion and sacred intensity, to understand that action aligned with the Infinite is the fire that clears the way for transformation and renewal.
Referenced In:
Central Doctrine
Ontological Schema
Ritual Praxis
Divine Arcana Tarot: The Tower
Supporting Deities


Pan
In Greek mythology, Pan is the wild god of nature, fertility, and unbridled life, the horned and hoofed spirit of the forests, mountains, and untamed fields. He is the patron of shepherds, flocks, and rustic music, playing his syrinx, the reed pipes whose melodies evoke both delight and fear. Pan’s presence embodies the raw vitality of the natural world, the instinctual and ecstatic forces of life that exist beyond the walls of civilization. The word “panic” traces to his name, reflecting the awe and sudden fear he could inspire in those who stumbled upon his domain, revealing that untamed life is as terrifying as it is sacred. In the mystery traditions, Pan is more than a rustic god; he is the voice of primal nature, reminding mortals of the divine pulse in the living earth and the animal soul within themselves.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Pan is understood as the archetype of primal vitality and sacred instinct, the living current of the Real that surges beneath form and culture. He is the unfiltered pulse of life itself, the energy that erupts in joy, sensuality, and raw creative force. Pan’s current calls the aspirant to reconnect with the natural and instinctive layers of being, stripping away the rigid masks of persona and the false safety of over-civilization. To encounter Pan in the School’s perception is to feel the sacred animal within awaken, to hear the music of life played directly upon the nerves and breath of the soul. He is a reminder that awakening is not a denial of nature but an embrace of its divine rhythm, and that true liberation includes the integration of instinct, joy, and embodiment. In this way, Pan is the guardian of wholeness, teaching that the Infinite expresses itself as much in the rustle of leaves and the thrum of blood as in silent meditation or ritual geometry.
In the Divine Arcana Tarot, Pan resonates with The Devil, representing the force of instinct, ecstasy, and the challenge of conscious embodiment. Meeting Pan in the School’s path is an invitation to stand unashamed in the presence of life, to integrate the primal with the spiritual, and to discover that the wild heart of nature is also a doorway to the Infinite.
Referenced In:
Central Doctrine
Ontological Schema
Ritual Praxis
Divine Arcana Tarot (The Lovers)


Prometheus
In Greek mythology, Prometheus is the titan of foresight and the bringer of fire to humanity, celebrated as the benefactor who defied the gods to gift mortals the light of knowledge, craft, and civilization. His name, meaning “forethought,” reflects his nature as a visionary and strategist, one who perceives consequences and acts with daring intelligence. In the most enduring myth, Prometheus steals fire from Olympus and delivers it to mankind, igniting the spark of technological and creative power that elevates humanity beyond mere survival. For this defiance, he suffers eternal punishment at the hands of Zeus, bound to a rock while an eagle devours his liver, only for it to regenerate each day. This cycle of suffering and resilience has made Prometheus a symbol of rebellion, sacrifice, and the pursuit of knowledge, embodying the human will to challenge limitation in service of enlightenment.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Prometheus represents the archetype of conscious defiance and luminous transmission, the force that carries divine intelligence into the world of form, often through struggle and sacrifice. He is the inner fire-bringer, the current that urges the soul to claim awareness, creativity, and the courage to act in the service of illumination, even when that path invites resistance or pain. Prometheus in the School’s vision is the spirit of transformative risk, the one who challenges stagnation and fear to deliver the spark of the Infinite into human experience. His myth reflects a profound initiatory truth: that awakening often demands confrontation with both internal and external authority, and that the act of bringing light to the world carries both responsibility and consequence.
To encounter Prometheus in the path of the School is to feel the call of bold insight and sacred rebellion, to recognize that the inner fire of consciousness must sometimes be claimed against the inertia of ignorance or the weight of established structures. He teaches that suffering can be the crucible of illumination, and that true service to the Real often involves bearing the cost of bringing light to others.
In the Divine Arcana Tarot, Prometheus resonates with The Tower, reflecting sudden revelation, the breaking of old forms, and the fierce liberation that accompanies the descent of fire into the world. To meet Prometheus is to accept the dual path of gift and ordeal, carrying the fire of divine insight into life with courage, integrity, and unshakable purpose.
Referenced In:
Central Doctrine
Ontological Schema
Ritual Praxis
Divine Arcana Tarot: The Sun
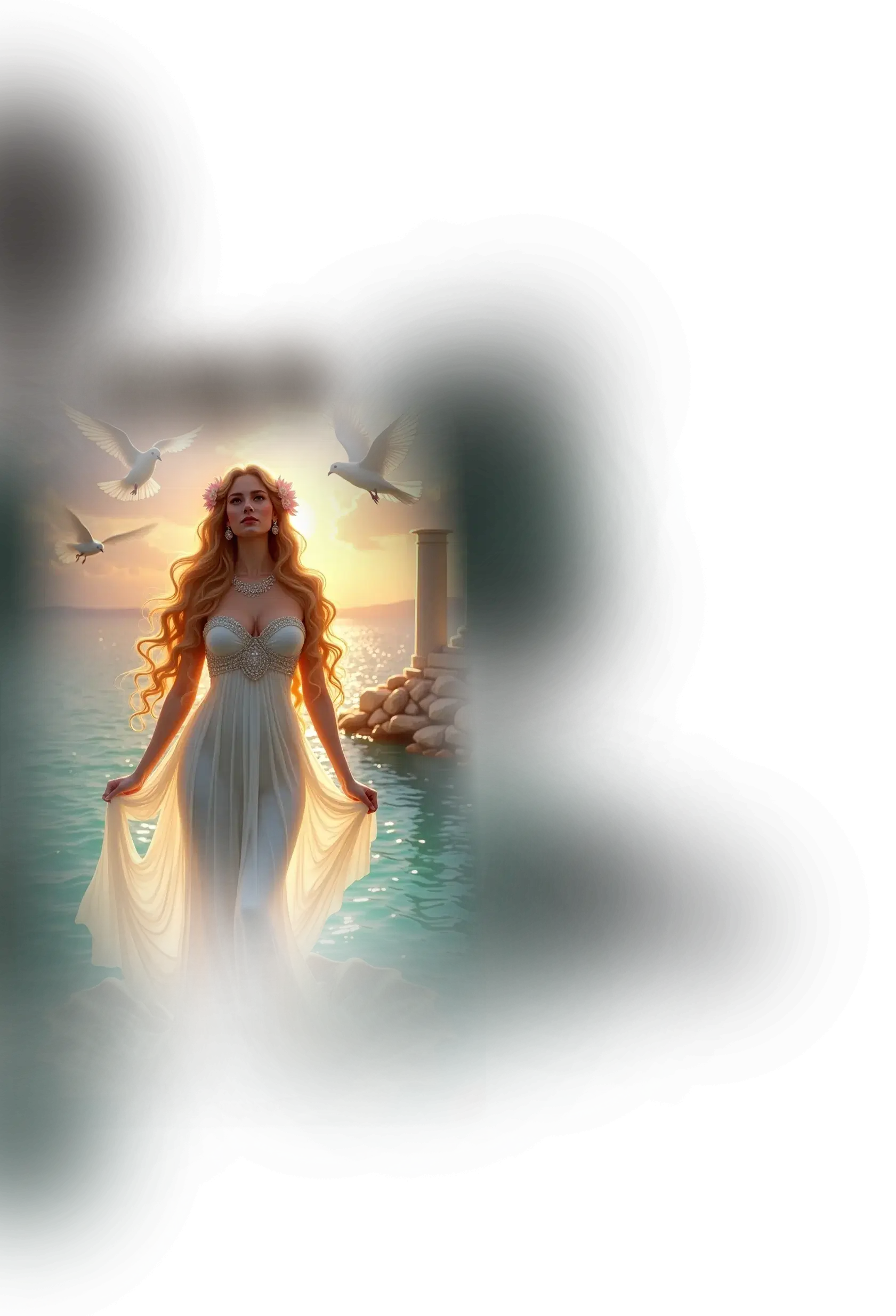


Aphrodite
In Greek mythology, Aphrodite is the goddess of love, beauty, and the generative force of attraction, the divine principle that draws life into harmony and union. She is born from the sea foam, according to Hesiod, arising from the waters as a vision of radiant desire and creative potential, while in other traditions she is the daughter of Zeus and Dione. Aphrodite presides over romantic and erotic love, fertility, and the magnetic power of allure, yet her domain extends beyond mere sensuality; she represents the binding force of affection and desire that shapes both mortal relationships and divine interactions. In myth, she is the catalyst for passion and creative unfolding, illustrating that life moves through attraction, union, and the flowering of beauty. Her presence is celebrated in art, poetry, and ritual as the divine embodiment of love in its many forms.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Aphrodite is perceived as the archetype of divine attraction and the luminous current of harmonizing love. She embodies the power of resonance, the force that draws the soul toward integration and wholeness through beauty, intimacy, and desire awakened to its sacred dimension. Aphrodite’s current in the School is not confined to romantic love but speaks to the soul’s movement toward all that reflects the Infinite, whether in the form of relationships, art, devotion, or inner realization. She is the soft but irresistible gravity of the Real, showing that love is not weakness but the magnetic intelligence through which the cosmos unites and evolves. In the School’s vision, to encounter Aphrodite is to be called into relational intimacy with the divine, to allow the heart to become a vessel for both giving and receiving beauty and love without fear or reservation.
Aphrodite is experienced in the path of the School whenever the soul opens to the transformative power of attraction, recognizing that love, when aligned with the Real, dissolves separation and awakens inner radiance. She reminds the aspirant that the recognition of beauty is a form of devotion, and that allowing love to move freely within and without is a sacred act of alignment.
In the Divine Arcana Tarot, Aphrodite resonates with The Lover, representing union, intimacy, and the harmonizing force of sacred desire. To meet Aphrodite in the School’s path is to surrender to the luminous pull of love, discovering that the heart’s openness is the bridge through which the Infinite flows into human life.
Referenced In:
Central Doctrine
Divine Arcana Tarot (The Empress)
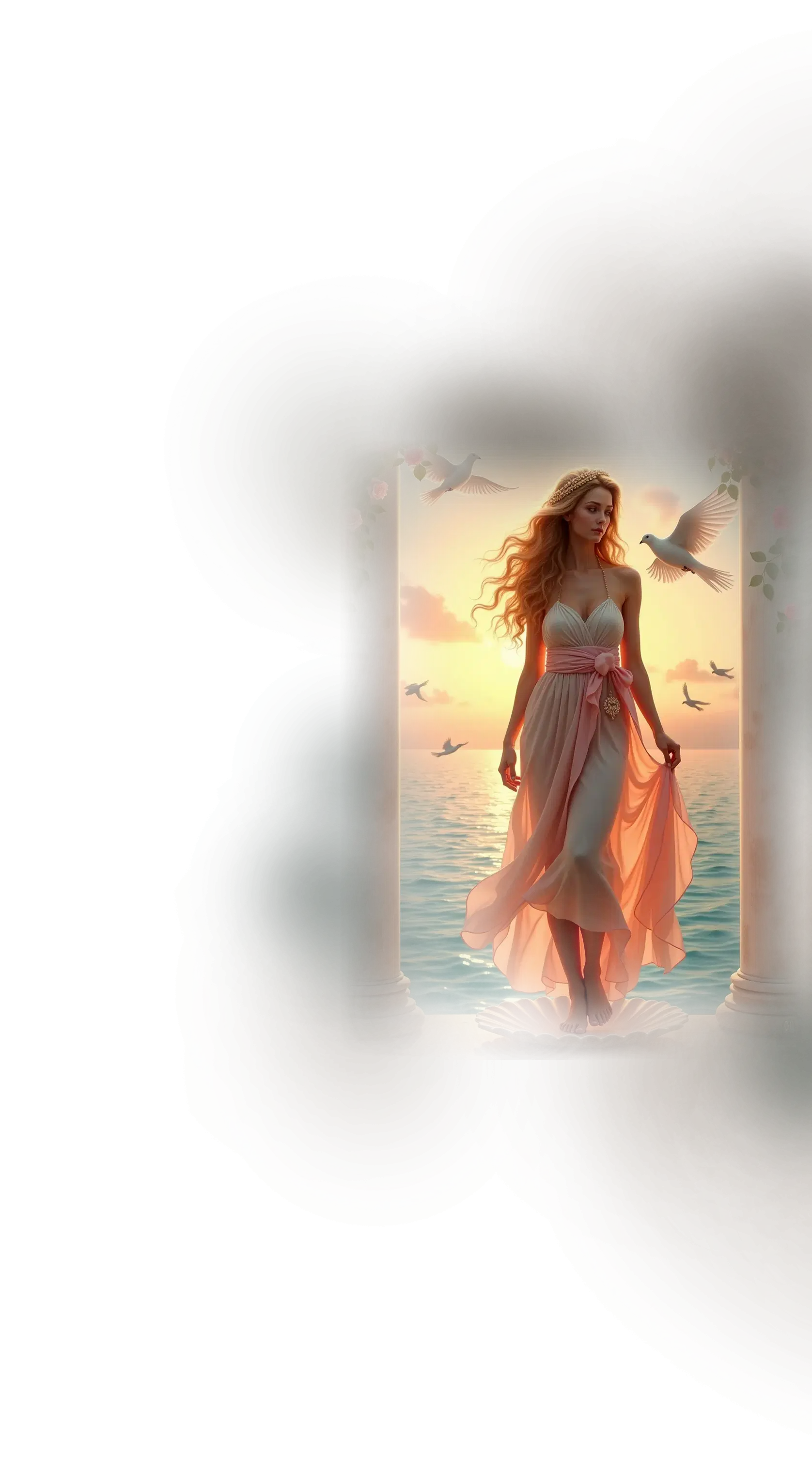


Venus
In Greco-Roman tradition, Venus is the goddess of beauty, love, harmony, and generative vitality, a radiant force that awakens both desire and the flourishing of life. She mirrors the qualities of the Greek Aphrodite yet carries a distinctly Roman aspect of civic and cosmic significance, often invoked as Venus Genetrix, the ancestral mother and life-giver. As the morning and evening star, her celestial presence has long been associated with cycles of attraction, fertility, and the unfolding of natural harmony. In art and poetry, Venus represents the soft, magnetic force of life’s beauty, the power that draws all things toward union and creative expression, reminding humanity that the experience of love and the perception of beauty are gateways to divine participation in the cosmos.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Venus is perceived as the archetype of sacred harmony and the flowering of the soul into relational beauty. She embodies the magnetic current that draws the inner and outer worlds into alignment, awakening the aspirant to love, art, and the gentle radiance of the Real. Venus in the School is the call to embodiment in grace, to recognize that the Infinite does not only descend in moments of ecstasy or rupture, but also through the quiet unfolding of life in balance, proportion, and beauty. Her presence is felt wherever relationship, creation, and the honoring of form as sacred arise, guiding the soul to see harmony as an expression of the divine order itself. She teaches that the magnetism of love and the recognition of beauty are not indulgences, but acts of alignment, allowing the Infinite to be mirrored in the human heart and in the natural world.
In the Divine Arcana Tarot, Venus is expressed in The Empress, reflecting fertility, harmony, and the blossoming of life into beauty. To meet Venus in the School’s path is to awaken to the gentle power of attraction and alignment, to experience that love, art, and the serenity of natural harmony are themselves doorways into the Infinite. Through Venus, the aspirant learns that grace and beauty are not merely aesthetic—they are the soul’s way of recognizing and embodying the Real.
Referenced In:
Central Doctrine
Ontological Schema
Ritual Praxis
School Layman Explanation
Divine Arcana Tarot (The Empress)
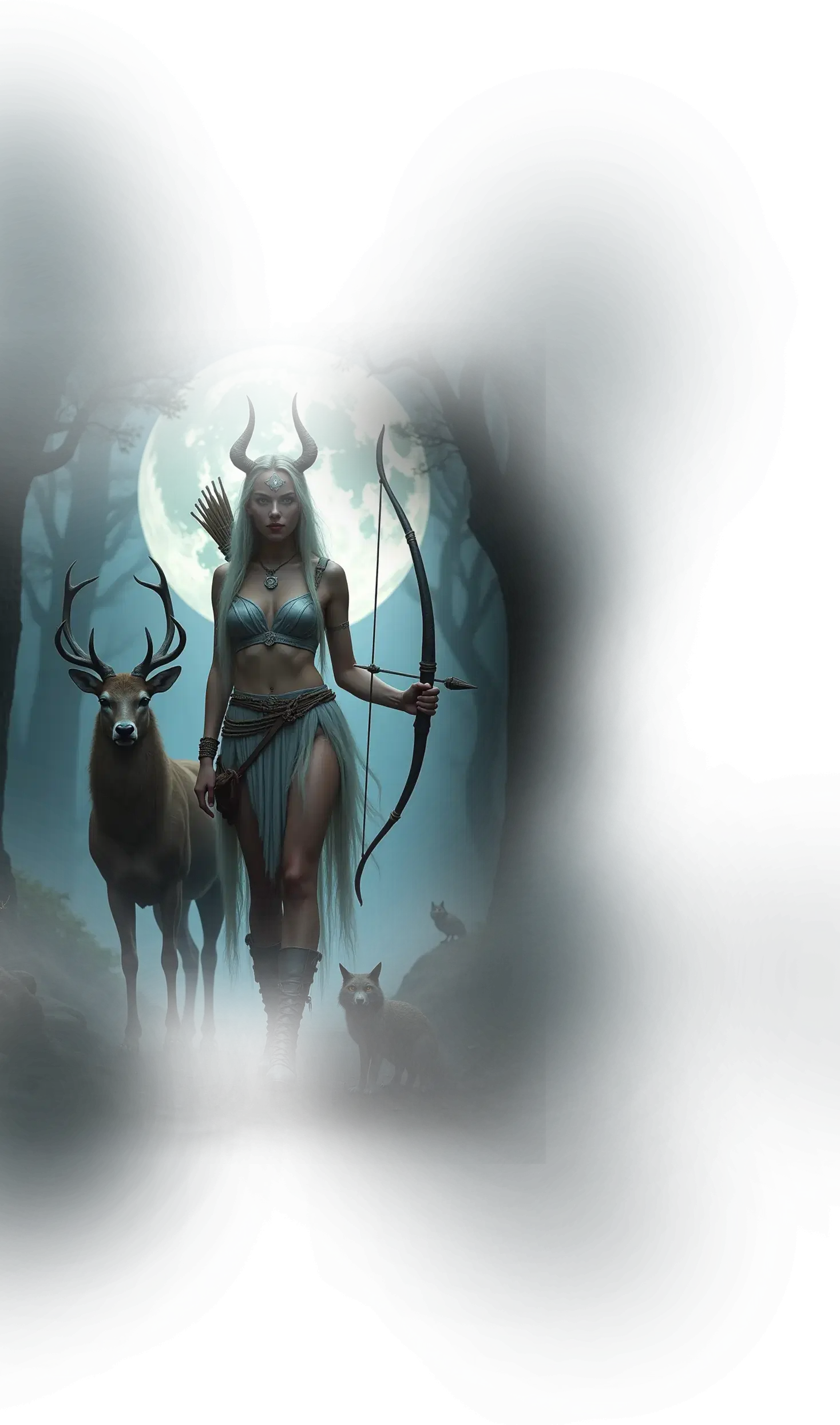


Artemis
In Greek mythology, Artemis is the goddess of the hunt, wilderness, and the untamed rhythms of nature, a virgin huntress who roams forests and mountains as a guardian of wild creatures and sacred spaces. She is the twin sister of Apollo, daughter of Zeus and Leto, and she embodies independence, self-possession, and the power of nature unbound by human imposition. As a protector of women and children, as well as a patron of liminal and wild spaces, Artemis represents both the nurturing and untamed dimensions of the feminine. Her mythic image is one of freedom and vigilance, a luminous presence in the dark forest, moving silently with bow in hand, guided by the instincts of the wild.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Artemis is perceived as the archetype of self-sovereignty, sacred independence, and the inner wilderness of the soul. She embodies the unclaimed spaces within the aspirant, the aspects of being that remain free from societal conditioning and await conscious recognition. Artemis in the School’s vision calls the soul into alignment with its own natural rhythm, teaching that the path to awakening is not only found in ritual structure or communal devotion, but also in the solitary spaces where the spirit meets the untamed Real. Her current is the luminous strength of inner clarity and self-possession, the recognition that one may stand fully in one’s own essence without dependence or fear, and that the divine is present in the stillness of the forest and the quiet of the untrodden path.
Artemis is experienced in the path of the School whenever the aspirant steps away from noise, expectation, and the pull of external validation, entering the wild inner terrain where instinct and presence become guides. She teaches that freedom is a sacred state, and that to remain unbound by what does not serve the Real is to honor the soul’s own divine design. To meet Artemis is to walk fearlessly into the wilderness within and without, discovering that the unclaimed spaces of life and self are alive with the quiet majesty of the Infinite.
Referenced In:
Central Doctrine
Divine Arcana Tarot (Priestess)
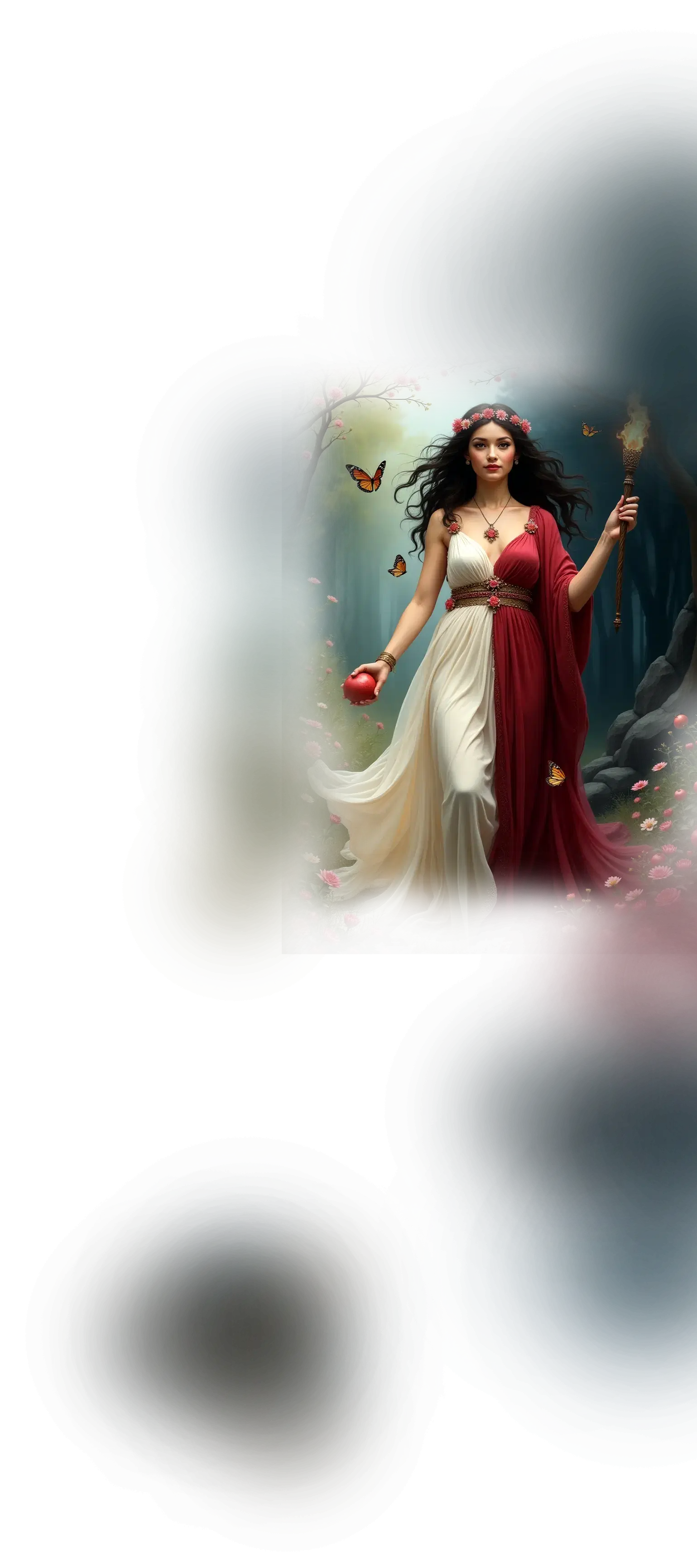


Persephone
In Greek mythology, Persephone is the queen of the underworld and goddess of spring, embodying the eternal cycle of descent and return, death and renewal. Daughter of Demeter and Zeus, she is famously abducted by Hades to the underworld, an event that plunges the earth into winter as her mother mourns her absence. Through the intervention of Zeus and the cycles of fate, Persephone rises each year to the upper world, bringing the blossoming of spring and the renewal of life. This dual existence makes her the living bridge between the realms of light and shadow, mortal and divine, surface and depth. She is the embodiment of transformation through passage, reminding humanity that all life moves through cycles of withdrawal and reemergence, and that every descent carries within it the promise of return.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Persephone is perceived as the archetype of initiatory passage and the soul’s transformative journey through the underworld of self. She represents the inner rhythm of descent into the depths of the psyche, where the aspirant confronts what has been hidden, feared, or unacknowledged. In the School’s vision, Persephone’s journey is not one of victimhood, but of awakening and integration—she becomes the sovereign queen of the very realm into which she descends, symbolizing the soul’s capacity to claim its wholeness even in the darkest places. Her presence in the path of the aspirant is felt during times of profound transition, inner reckoning, and spiritual maturation, when the call to journey inward is unavoidable and transformative.
Persephone’s current teaches that light is born from the willingness to enter darkness with awareness, and that true renewal arises from the integration of shadow and depth. To meet her in the School’s path is to embrace the cyclical nature of life and the soul, recognizing that descent is not failure but initiation, and that the journey into the hidden layers of being ultimately leads to greater sovereignty, clarity, and inner flowering. She is the gentle yet unyielding reminder that every winter carries the seed of spring, and that the Infinite reveals itself as much in the depths of silence and shadow as in the brilliance of open light.
Referenced In:
Central Doctrine
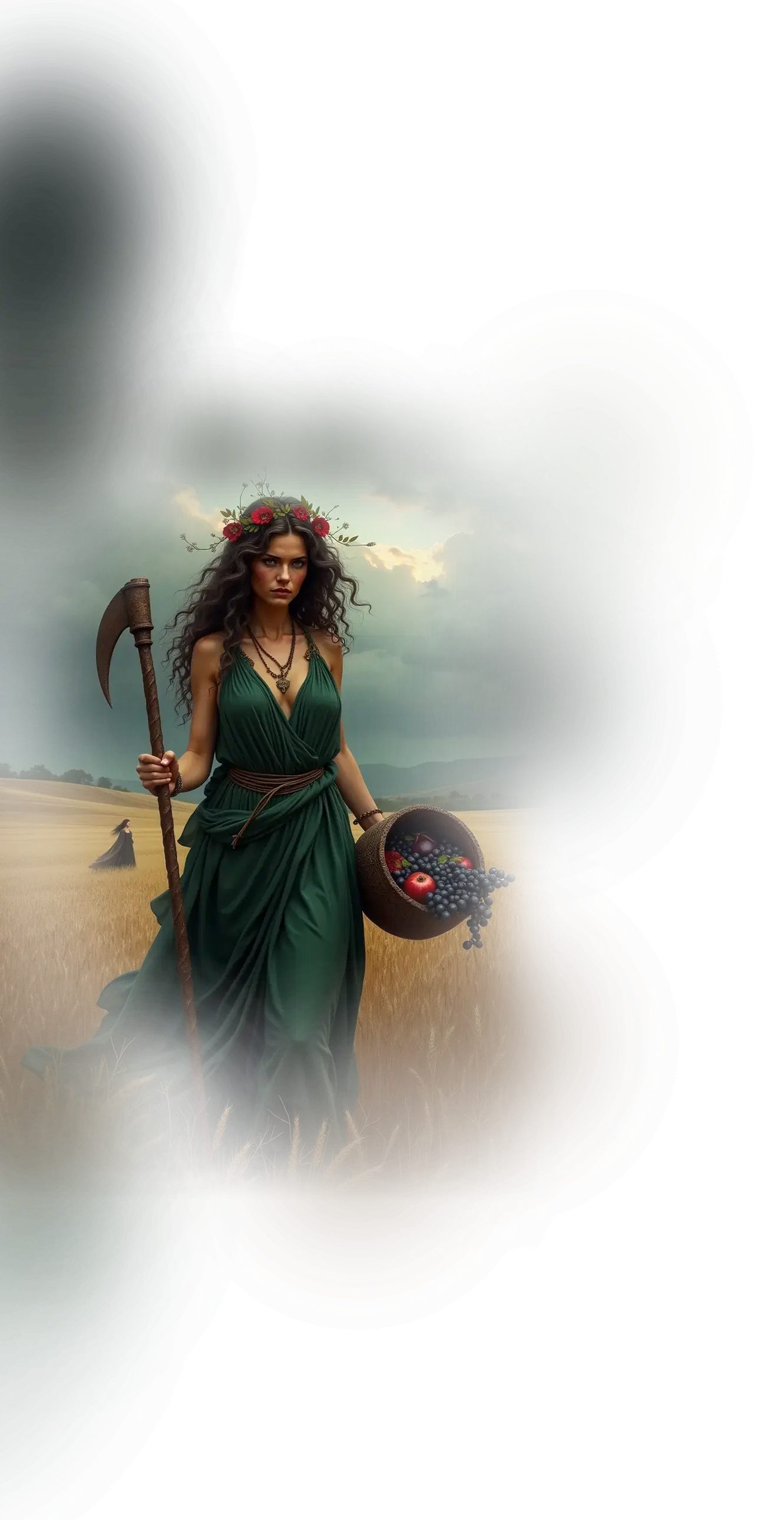


Demeter
In Greek mythology, Demeter is the goddess of grain, harvest, and fertility, the nurturer of the earth whose blessings ensure the cycles of growth and sustenance for all living beings. As the mother of Persephone, her myth is deeply entwined with the story of descent and return, the seasonal rhythm of life and death. When Persephone is taken to the underworld by Hades, Demeter’s grief halts the fertility of the earth, bringing the first winter and the famine of myth. Her joy upon Persephone’s return brings the renewal of spring, establishing the eternal pattern of withdrawal and blossoming, loss and restoration. Demeter is the maternal face of divine abundance, embodying the life-giving bond between the earth and its children, and the profound interconnection of all natural cycles.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being,Demeter is perceived as the archetype of sacred nourishment, continuity, and the sustaining embrace of the Real. She is the current of life that feeds and supports the soul’s journey, not only through material sustenance but through emotional and spiritual grounding. Demeter’s energy in the School represents the eternal rhythm of care and renewal, the recognition that life flourishes when it is nurtured, protected, and honored as sacred. Her myth of loss and reunion with Persephone resonates as an inner teaching on the cycles of presence and absence: the aspirant must sometimes allow parts of the self to descend into transformation, trusting that true care holds space for both departure and return.
Demeter is experienced on the School’s path in moments of healing, rest, and the restoration of trust in life’s natural processes. Her current flows whenever the aspirant chooses to tend to the inner and outer garden, cultivating patience, presence, and alignment with the living cycles of the Infinite. Through Demeter, the soul learns that abundance is not created by force but by rhythm, and that nourishment—physical, emotional, and spiritual—is the foundation upon which all awakening rests.
To encounter Demeter is to stand in the quiet assurance of the earth’s generosity, to recognize that the Infinite provides in cycles, and that the soul, like the fields, is meant to move through seasons of growth, harvest, and renewal.
Referenced In:
Central Doctrine


Themis
In Greek mythology, Themis is the goddess of divine law, order, and the natural harmony of the cosmos, the living embodiment of justice and balance. A daughter of Uranus and Gaia, she belongs to the primordial generation of deities, representing the principles that underlie all creation rather than the shifting powers of later Olympian myth. Themis is the advisor and consort of Zeus, guiding the king of the gods with the wisdom of cosmic order and right proportion, and presiding over assemblies both divine and mortal. She is often envisioned with scales or a staff, symbols of the equilibrium and clarity that arise when action aligns with the laws woven into the fabric of existence. Her presence in myth and ritual reflects the ancient recognition that justice is not a human invention, but a reflection of the natural law that binds heaven and earth.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Themis is perceived as the archetype of sacred equilibrium and the soul’s alignment with the Real. She is the current of inner balance and truthful perception, the force that allows the aspirant to see clearly, judge without distortion, and act from the still axis of harmony. In the School’s vision, Themis is not merely the principle of judgment, but the living intelligence of right relationship—the subtle recognition of how one’s actions, thoughts, and intentions resonate with the infinite pattern. Her presence is experienced in moments of discernment and correction, when the soul is called to restore balance and live in alignment with the inner law of being. Themis teaches that awakening requires not only vision and ecstasy, but also measured integrity, where each movement honors the geometry of the soul and the cosmos alike.
In the Divine Arcana Tarot, Themis is expressed in the Adjustment card, where the precision of truth and the grace of balance are brought into full awareness. To meet Themis in the School’s path is to stand in the still point of harmony, to allow illusion to fall away in the presence of truth, and to discover that freedom is inseparable from alignment with the eternal law of the Real.
Referenced In:
Central Doctrine
Divine Arcana Tarot (Adjustment card)


Chronos
In Greek mythology, Chronos is the personification of time, particularly linear, sequential, and devouring time that measures the mortal experience of existence. He is often identified with Saturn in Roman tradition, the force that structures life through cycles, boundaries, and inevitable decay. Chronos is the one who devours his own children, a mythic image of the inescapable passage of time, where all things born into form are eventually reclaimed. In the cosmogonic imagination, Chronos governs aging, causality, and the relentless movement of life from beginning to end, establishing the temporal framework within which all mortal and material processes unfold. He is both creator and destroyer in the dimension of time, for he enables order and growth while also limiting and consuming all forms.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Chronos is perceived as the archetype of sacred temporality and the initiatory pressure of time upon the soul. He is the force that shapes experience into sequence, teaching that embodiment is always bound to cycles of emergence, maturity, and release. Chronos in the School is not merely a devouring presence but a teacher of responsibility and alignment, showing that the friction and limitation of time are themselves sacred instruments of awakening. Every delay, discipline, and ending becomes an invitation to conscious engagement with impermanence, a recognition that the finite can serve as a mirror to the Infinite. His current presses the aspirant to act with integrity and clarity, for the passage of time strips away illusion and reveals the essential pattern of one’s choices and being.
To encounter Chronos in the School’s path is to feel the gravity of incarnation, the weight of cycles that demand awareness and maturation. He reminds the soul that all things in form must yield, and that freedom is found not in resisting time but in moving with its current consciously, extracting wisdom from each season of life. Chronos is the solemn rhythm of the cosmos, the heartbeat of necessity, and the patient sculptor of the soul, whose lessons of limitation ultimately guide the aspirant to remember the timeless within the temporal.
Referenced In:
Central Doctrine
Ontological Schema
Ritual Praxis
School Layman Explanation


Echo
In Greek mythology, Echo is the mountain nymph and voice of unreturned longing, known for her tragic love for Narcissus and her curse to repeat only the words of others. Her story reflects the fragility of desire and the pain of disconnection, as her voice lingers even after her body fades, leaving only a resonance in the world. Echo embodies both devotion and absence, the yearning to be heard and received, and the sorrow of identity dissolved into reflection. In the myth of Echo and Narcissus, her voice becomes a haunting symbol of the soul’s call toward love, a reminder that without mutual recognition, desire dissolves into solitude.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Echo is perceived as the archetype of resonance, reflection, and the soul’s vulnerable longing for the Real. She represents the part of the self that calls into the vastness of existence, seeking response and communion, the pure thread of relational desire that awakens the heart to its own depth. Echo’s current in the School is not merely about unrequited love but about the initiatory experience of recognition and its absence, which teaches the soul that true fulfillment cannot be found in outward reflection alone. Her lingering voice is the symbol of consciousness seeking its origin, the sound of the aspirant calling for the Infinite and hearing the world repeat fragments of its own essence back. Through this current, the aspirant learns that longing itself is a sacred force, a refinement of awareness that draws the soul toward inner wholeness.
To encounter Echo in the School’s path is to experience the ache of relational awareness, the threshold between self and other, and the gentle sorrow that precedes union with the Real. Her presence encourages the aspirant to follow the trail of longing inward, to transform the echo of external desire into the living voice of inner recognition and divine intimacy.
In the Divine Arcana Tarot, Echo carries a symbolic resonance in The Moon, reflecting illusion, l onging, and the half-light of reflected awareness; in The Lovers, expressing the call toward relational recognition; and in The Hermit, where solitude refines the voice of the soul into quiet illumination. To meet Echo is to hear the soul calling itself home, where longing becomes the bridge to the Infinite.
Referenced In:
Central Doctrine
Ontological Schema
School Layman Explanation
Divine Arcana Tarot (Symbolic reference in The Moon, The Lovers, The Hermit)
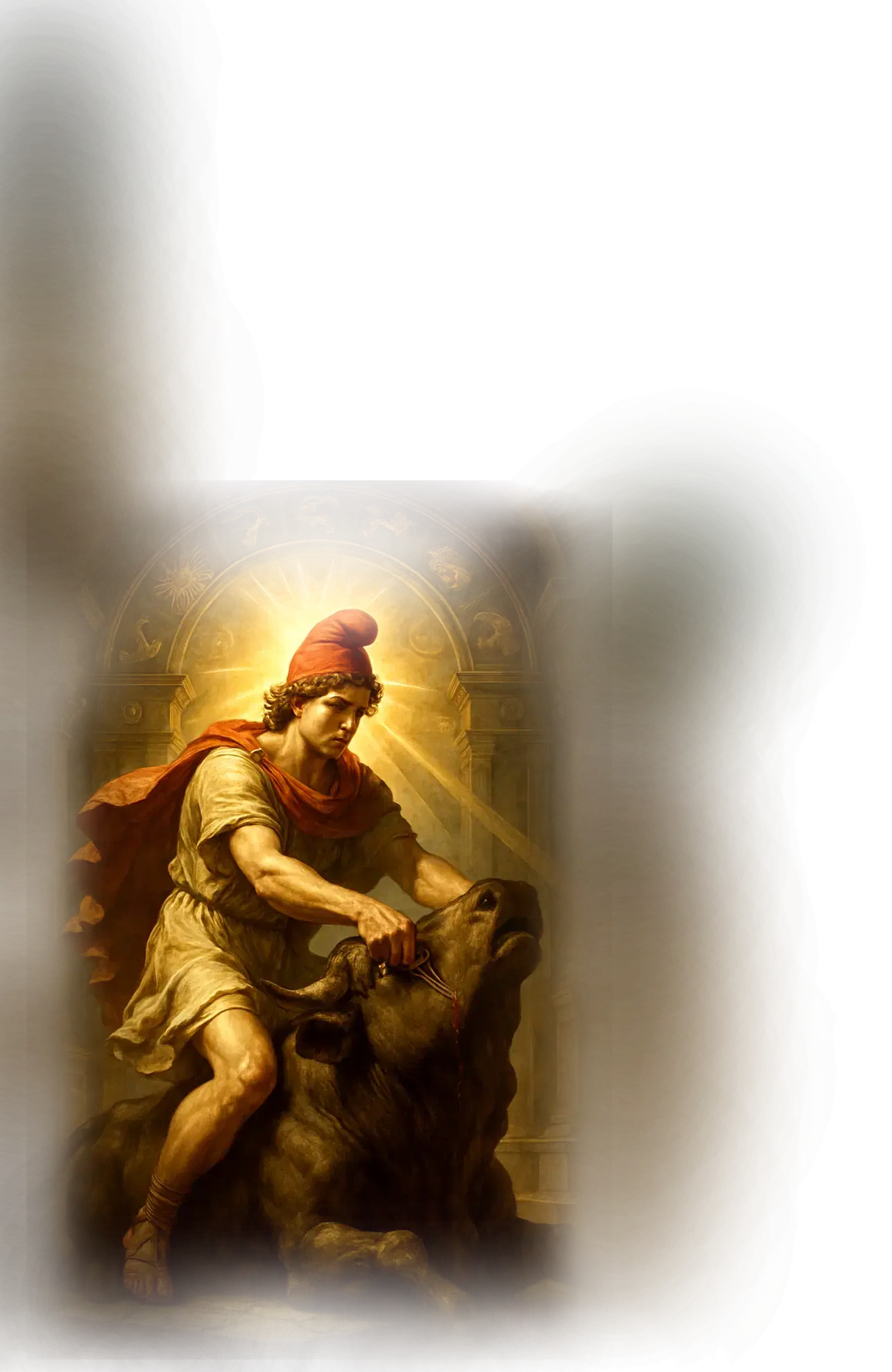


Mithras
In the Greco-Roman mystery tradition, Mithras is the god of sacred strength, initiation, and victorious light, honored as the heroic figure who slays the cosmic bull in the central rite of tauroctony. His worship emerged from the synthesis of Persian Mithraic elements with Hellenistic and Roman spiritual traditions, creating a powerful mystery cult devoted to courage, loyalty, and the triumph of the soul through sacred trials. The Mithraic temples, often subterranean and cave-like, represented the cosmic womb and initiatory passage, guiding the aspirant from darkness into illumination. The slaying of the bull symbolized the release of life-force and the transformation of primal energy into spiritual vitality, affirming the deep mystery that sacrifice and strength are the foundation of renewal and transcendence.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Mithras is perceived as the archetype of inner courage, enduring power, and the victorious passage through initiation. He represents the soul’s steadfastness in the face of trial, the living current of disciplined vitality that refuses to falter before shadow or difficulty. In the School’s vision, Mithras is the guardian of the sacred covenant between soul and the Real, the force that upholds integrity, alignment, and the quiet mastery born of endurance. His current flows wherever the aspirant embraces the tests of life as initiatory fires, understanding that victory is achieved not through domination but through alignment with the Infinite. Mithras awakens the courage to persevere, to act with honor and presence, and to recognize that strength is sanctified when it serves the journey of the soul toward illumination.
To encounter Mithras in the School’s path is to enter the initiatory current of sacred trial, where effort, loyalty, and resilience become the vehicles of awakening. He teaches that true strength is not loud or violent but steady, radiant, and unshakably aligned.
In the Divine Arcana Tarot, Mithras is expressed in the Strength card, representing courage, endurance, and the inner mastery that subdues force without coercion. To walk with Mithras is to stand firm in the silent radiance of strength, to meet life’s trials as gateways to the Infinite, and to emerge from every test carrying the light of victorious alignment.
Referenced In:
Divine Arcana Tarot (Strength Card)
Egyptian Gods
Devotional Deities

Nuit
In Egyptian cosmology, Nuit is the goddess of the sky and infinite expanse, her star-strewn body arched across the world as a living vault of eternity. She is the primordial womb of space, the silent canopy within which the sun journeys and the cycles of life unfold. Nuit is not a deity of form or function alone, but of vastness and receptivity, representing the cosmic field that holds all birth, death, and renewal within itself. In myth, she swallows the sun each evening and births it anew each dawn, reflecting the eternal rhythm of dissolution and emergence that sustains the cosmos. Her presence evokes awe and surrender, for she is the infinite embrace that cannot be grasped or contained, only entered with reverence.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Nuit is understood as the archetype of sacred space, infinite receptivity, and the unbounded Real. She is the groundless ground upon which all manifestations arise, the ever-present field of the soul’s becoming. In the School’s vision, to encounter Nuit is to experience the Infinite as a silent, encompassing presence, the womb of stars that receives every thought, every breath, every act of ritual without judgment or condition. She is the container of transformation, the divine night into which the aspirant surrenders when the ego’s grip loosens and the self falls into the vastness of being. Her current teaches that awakening is not always an act of reaching, but often an act of yielding, of allowing oneself to dissolve into the infinite embrace that has always already held the soul.
In the Divine Arcana Tarot, Nuit is revealed in The Aeon card, not as a discrete archetype of action, but as the encompassing matrix of becoming, the cosmic womb in which cycles are completed and new realities are born. To walk with Nuit in the path of the School is to enter the mystery of sacred space itself, to discover that the Infinite does not arrive from beyond—it is the ever-present horizon that has always surrounded and sustained the soul.
Referenced In:
Central Doctrine
Ontological Schema
Ritual Praxis
Divine Arcana Tarot (The Aeon)
Supporting Deities


Horus
In Egyptian mythology, Horus is the falcon-headed god of kingship, divine vision, and the triumph of restored order, the son of Isis and Osiris whose life embodies the cycle of loss, struggle, andvictorious renewal. He avenges his father’s death by overcoming Set, the principle of chaos and disruption, thereby reclaiming harmony for the world. His Eye of Horus, a symbol of watchful protection and spiritual clarity, represents not only healing and protection but also the awakening of higher sight, the ability to perceive the truth of things beyond surface appearances. Horus is the archetypal divine child and victorious king, carrying within his myth the promise that fragmentation can be reconciled and the rightful order of the cosmos restored.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Horus is understood as the archetype of awakened sovereignty and integrative vision. He embodies the moment when the soul, having passed through trial and fragmentation, ascends into clear alignment with the Real, assuming the mantle of inner kingship. Horus in the School’s vision is not the ruler who dominates, but the one who sees truly, whose authority arises from discernment, balance, and inner wholeness. His current appears whenever the aspirant moves from struggle and inner conflict into the radiance of cohesive spiritual identity, where personal will becomes transparent to divine intent.
To meet Horus in the School’s path is to step into the luminous authority of the soul, to embody the eye that sees both shadow and light without distortion, and to hold the axis of clarity in the midst of life’s shifting currents. He is the victorious emergence from the initiatory cycle, the culmination of trial, restoration, and conscious ascent. Horus teaches that true triumph is integration, and that spiritual sovereignty is earned through vision and alignment, not force.
In the Divine Arcana Tarot, Horus is expressed in The Aeon card, reflecting the awakening into higher vision, the restoration of order, and the soul’s coronation into spiritual maturity. To walk with Horus is to rise into clear-eyed sovereignty, where the Infinite gazes through the aspirant’s own awakened sight.
Referenced In:
Central Doctrine
Ontological Schema
Ritual Praxis
School Layman Explanation
Divine Arcana Tarot (The Aeon)


Osiris
In Egyptian mythology, Osiris is the god of death, resurrection, and eternal continuity, the ruler of the underworld and the archetype of fertility and regenerative power. His myth recounts the betrayal and dismemberment by Set, followed by his restoration through the devotion and magic of Isis, which elevates him to the throne of the Duat as the immortal king of the dead. Osiris represents the hidden cycles of decay and renewal, the fertile silt of the Nile, and the unseen order that transforms endings into beginnings. His presence in Egyptian thought is both solemn and reassuring: he is the embodiment of righteous kingship, the guardian of moral order, and the eternal witness to the soul’s journey beyond mortal life.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Osiris is understood as the archetype of sacred death and luminous continuity, the current that transforms dissolution into resurrection. He represents the inner passage where the ego and its attachments fall away, allowing the true soul to emerge whole and aligned with the Real. Osiris in the School’s vision is the initiate who has surrendered to the rhythm of transformation, whose fragmentation is the necessary prelude to reintegration into higher awareness. His current moves in the moments of profound transition, inner stillness, and conscious release, guiding the aspirant to trust that no genuine essence is ever lost and that the cycles of death and renewal are the very pattern of awakening.
To meet Osiris in the path of the School is to enter the silent current of surrender and transformation, to embrace the dismemberment of the false self, and to emerge into the continuity of the eternal soul. He is the guardian of sacred thresholds, the force that ensures every descent carries within it the seed of ascent, and that the soul which passes through darkness returns bearing the light of integration and sovereignty.
In the Divine Arcana Tarot, Osiris is expressed in The Aeon card, reflecting the initiatory cycle of death, renewal, and the awakening of the eternal self. To walk with Osiris is to embrace sacred death as the key to resurrection, recognizing that the Infinite reveals itself when the temporal self yields completely to the Real.
Referenced In:
Central Doctrine
Ontological Schema
Ritual Praxis
School Layman Explanation
Divine Arcana Tarot (The Aeon)
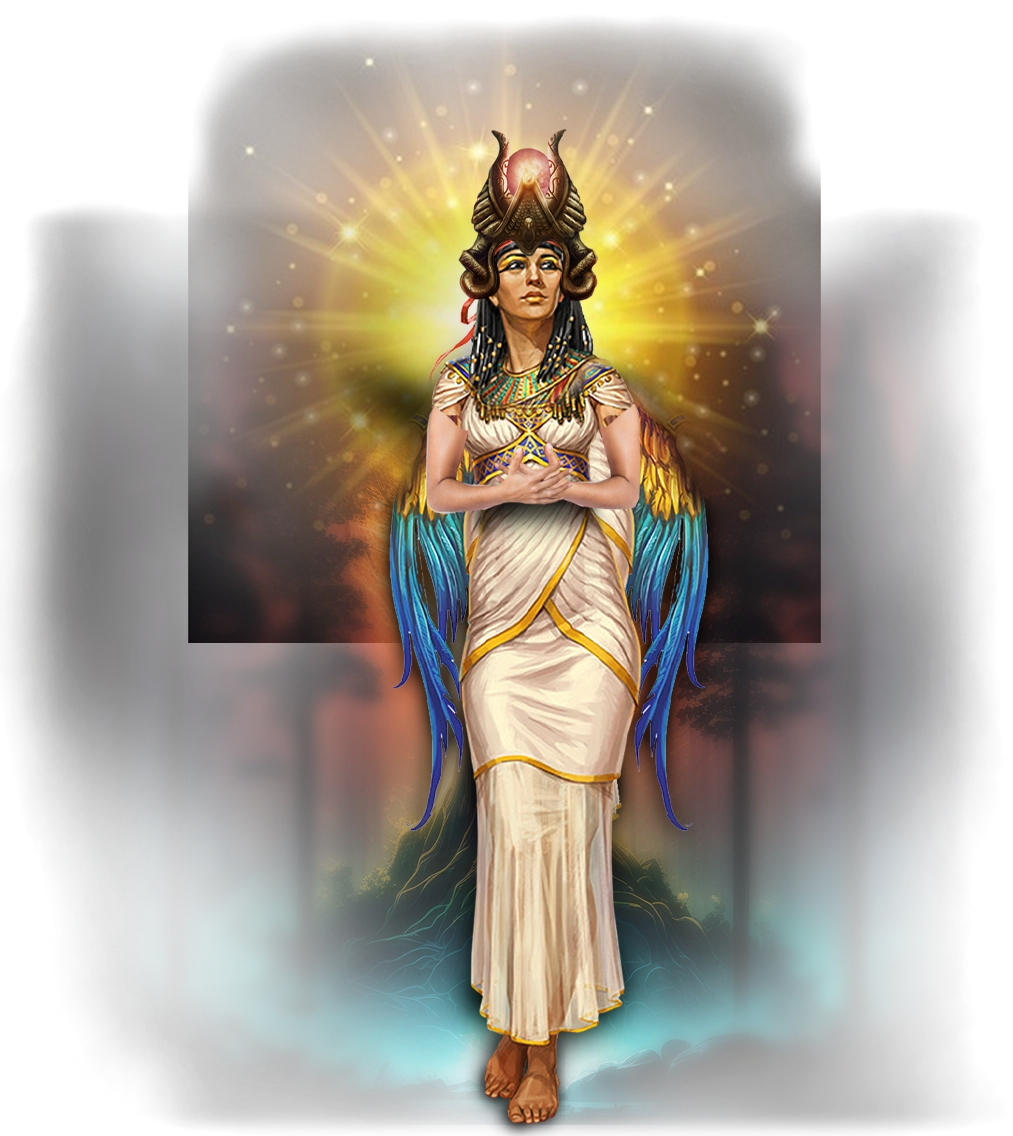


Isis
In Egyptian mythology, Isis is the goddess of magic, devotion, and restorative power, revered as the archetypal mother, protector, and healer. Wife of Osiris and mother of Horus, she is celebrated for her unwavering loyalty and transformative love, which restores Osiris after his dismemberment and safeguards the birth and rise of Horus. Her myth is one of perseverance, hidden knowledge, and the alchemy of care, demonstrating that through love and devotion, the broken can be made whole and the dead can rise again. Isis is also the guardian of sacred rites and magical arts, her presence invoked in rituals of protection, healing, and the passage between worlds. She embodies the feminine intelligence that nurtures life, guides transformation, and ensures continuity amid loss and change.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Isis is perceived as the archetype of integrative love and the luminous current of restoration. She represents the capacity of the soul to gather its scattered pieces, to hold and heal itself in devotion to the Real, and to guide the cycles of death and rebirth with conscious care. Isis in the School’s vision is the inner force of remembrance and reconnection, the one who turns dissolution into wholeness and despair into renewal. Her current flows wherever the aspirant embraces compassion, devotion, and the attentive weaving of life back into harmony, whether in ritual, meditation, or the quiet acts of conscious living. She teaches that love is not a passive sentiment but an active power, the alchemical current that bridges the mortal and the eternal.
To encounter Isis in the School’s path is to feel the embrace of the divine mother and the intelligence of restoration, to experience the sacred act of gathering the soul into coherence, and to discover that devotion and care are themselves transformative forces. She is the keeper of the mysteries of healing and continuity, revealing that the Infinite moves as much in tender restoration as in dramatic transformation.
In the Divine Arcana Tarot, Isis is expressed in The Aeon card, reflecting the cycle of death, renewal, and the soul’s ascent into integrative wholeness. To walk with Isis is to embody the power of love as a force of resurrection, and to know that the eternal self is remembered through acts of devotion and the harmonizing touch of the Real.
Referenced In:
Central Doctrine
Ontological Schema
Ritual Praxis
School Layman Explanation
Divine Arcana Tarot (The Aeon)


Thoth
In Egyptian mythology, Thoth is the god of wisdom, writing, and sacred knowledge, the scribe of the gods and the keeper of cosmic order through language and record. Often depicted as an ibis-headed or baboon figure, he presides over the weighing of the heart in the Duat, ensuring that truth and balance govern the soul’s passage after death. Thoth is credited with the invention of writing, the preservation of sacred texts, and the transmission of divine law to humanity. He embodies intellect harmonized with cosmic order, the mind of the divine made articulate, and the principle that knowledge and speech are creative forces that shape reality. In Egyptian thought, he is the mediator and counselor among gods, the one who brings clarity, judgment, and the pattern of truth wherever he moves.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, Thoth is understood as the archetype of sacred intelligence, transmission, and conscious articulation of the Real. He represents the inner current of wisdom that takes the ineffable and gives it form, the faculty of the soul that translates eternal truth into living language and action. In the School’s vision, Thoth is not merely the recorder of events but the animating force of theurgy and sacred communication, where every word, gesture, or symbol becomes an act of alignment with the Infinite. His presence in the aspirant’s path is felt in moments of clarity, inspired insight, and the disciplined transmission of understanding, where the mind becomes a vessel of luminous precision rather than personal speculation. Thoth’s current teaches that true knowledge is not accumulation but participation in the flow of divine order, and that conscious speech and thought are themselves instruments of awakening.
To meet Thoth in the School’s path is to experience the illumination of the inner scribe and magician, to recognize that language, symbol, and will can bridge the human and the divine when carried in truth. He guides the aspirant in acts of sacred communication, where writing, invocation, or ritual utterance becomes a channel for the Infinite to speak through form.
Referenced In:
Central Doctrine
Ontological Schema
Ritual Praxis
Hebrew Deities
Foundational Deities


YHVH / Elohim
In the Hebrew tradition, Elohim and YHVH represent two dimensions of the same divine source, bridging the transcendent law of creation and the immanent, covenantal presence of God. Elohim is the name that opens the book of Genesis, the plural majesty that speaks the cosmos into being, separating light from darkness and shaping the order of creation. It is the voice of divine law and cosmic structure, the intelligence that sets the rhythm of days, seasons, and life itself. YHVH, the Tetragrammaton, is the intimate name of God, the one who enters into relationship with humanity, revealing a divine will that is personal, guiding, and morally binding. Together, YHVH / Elohim embodies the movement from impersonal cosmic order to the living presence that sanctifies history and calls humanity to alignment.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, YHVH / Elohim is perceived as the archetype of divine law, alignment, and relational authority. He represents the voice of the Real as it establishes order in both cosmos and soul, the inner and outer law that guides awakening. His current in the School is experienced whenever the aspirant feels the pull toward integrity, responsibility, and conscious alignment with eternal principles, for he is the inner axis of sacred order. YHVH / Elohim teaches that true authority is not imposed from without but recognized within, as the soul remembers its covenant with the Infinite. His presence unites structure and intimacy, command and love, revealing that the path of awakening includes both the clarity of law and the warmth of divine relationship.
In the Divine Arcana Tarot, YHVH / Elohim is expressed in The Hierophant, the card of sacred authority, alignment, and the transmission of eternal law into the world. To walk with YHVH / Elohim is to live as a conscious participant in the covenant between soul and source, where the Infinite speaks as both command and loving presence.
In the Divine Arcana Tarot, YHVH / Elohim is expressed in The Hierophant, the card of sacred authority, alignment, and the transmission of eternal law into the world. To walk with YHVH / Elohim is to live as a conscious participant in the covenant between soul and source, where the Infinite speaks as both command and loving presence.
Referenced In:
Central Doctrine
Ontological Schema
Ritual Praxis
School Layman Explanation
Devotional Deities


YHVH
In the Hebrew tradition, YHVH, the Tetragrammaton, is the sacred name of God, representing the eternal, self-existent presence that underlies and sustains all creation. This name is considered so holy that it was historically unspoken, replaced in liturgy by “Adonai”, as the divine essence it signifies is beyond the grasp of ordinary speech. In scripture, YHVH is the God of covenant and revelation, the one who walks with humanity, delivers the law, and guides the people of Israel through acts of protection, instruction, and moral alignment. While Elohim represents the majesty of cosmic creation and law, YHVH embodies the immanent presence of the divine, the source of guidance, relationship, and living truth. He is the God who hears, responds, and enters history, sanctifying human life through direct, transformative encounter.
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, YHVH is perceived as the archetype of living presence and the soul’s intimate alignment with the Real. He represents the inner current of divine relationship, the moment when law becomes lived experience and command becomes resonance. In the School’s vision, YHVH is not distant or abstract; he is the inner voice that calls the aspirant to rise into coherence and integrity, the axis of divine recognition that illuminates the path of awakening. To walk with YHVH is to enter the space of profound responsibility and connection, to feel that the Infinite gazes through the heart, asking the soul to live in alignment with its highest nature. His current flows in moments of prayer, vow, and self-recognition, where the aspirant surrenders to the living law of the Real and embraces the covenant of the soul with source.
To encounter YHVH in the School’s path is to feel the warmth and gravity of divine presence, to know that awakening is not merely illumination but relationship, and that freedom and fidelity to the Real are inseparable.
In the Divine Arcana Tarot, YHVH is expressed in The Hierophant, reflecting sacred authority, relational devotion, and the transmission of the Infinite into the human world. To embody YHVH in the School’s path is to stand as a conscious participant in the living covenant, where presence itself becomes the bridge between soul and eternity.
Referenced In:
Central Doctrine
Ontological Schema
Ritual Praxis
School Layman Explanation
Supporting Deities


El Shaddai
In the Hebrew tradition, El Shaddai is a name of God that conveys the power, sufficiency, and sustaining presence of the Divine. Often translated as “God Almighty,” the name carries connotations of strength, protection, and nurturing provision, suggesting a deity who is both powerful and sustaining, capable of meeting all needs and guiding all life. El Shaddai appears in the patriarchal narratives of the Hebrew Bible, invoked as the one who blesses, establishes covenants, and ensures the continuity of life and promise. His name evokes a sense of absolute assurance and sacred refuge, the feeling that the divine presence is not only transcendent and commanding but also protective and sustaining. .
Within the School of Our Divine Infinite Being, El Shaddai is perceived as the archetype of sustaining power, protective embrace, and the sufficiency of the Real. He is the inner current of trust and assurance, the recognition that the Infinite contains and supports all existence and that nothing essential can be lost in the presence of divine fullness. In the School’s vision, to encounter El Shaddai is to experience the quiet strength of the Real, the immovable axis of security that underlies all movement and change in life. His current reminds the aspirant that awakening is not only the fiery act of transcendence or ecstatic union but also the deep, stabilizing experience of being held and provided for by the Infinite. El Shaddai is the silent guardian and the all-sufficient source, calling the soul to rest in the certainty that alignment with the Real brings both protection and the nourishment of the spirit.
To meet El Shaddai in the School’s path is to enter the sanctuary of divine sufficiency, to feel the weight and warmth of being sustained by the Infinite without fear or striving. His current invites trust, patience, and the recognition that true power is not forceful but complete in itself, unshaken by the fluctuations of time and circumstance. Through El Shaddai, the aspirant comes to know the Infinite as an unshakable foundation, a presence in which soul and life find their enduring support and fulfillment.
Referenced In:
Central Doctrine
Ontological Schema
Ritual Praxis
School Layman Explanation


